304不锈钢由于具有良好的耐腐蚀性、耐高温、加工性能好等优点被普遍应用在航空航天、建筑装饰、石油化工、机械、汽车等[1-3]很多领域,但其在酸性介质中不可避免地会遭到腐蚀[4-6].因此,提高不锈钢在酸性介质中的耐蚀性是一个亟待解决的问题.目前,控制腐蚀最方便、最快捷的方法是添加缓蚀剂.国内已有很多种缓蚀剂应用于不锈钢的缓蚀,但对缓蚀剂复配的研究却很少见报道.因此,通过对不同类型缓蚀剂及缓蚀剂复配对于不锈钢的耐蚀性研究,发现高效、经济和绿色环保型缓蚀剂[7],对减少因腐蚀造成的经济损失具有重要的意义.
近年来国内外研究学者对于缓蚀剂和缓蚀机理进行了大量研究.K.Zakaria等[8]利用失重法、电化学方法等研究了两种有机化合物对于碳钢在盐酸溶液中的缓蚀性,结果表明两种缓蚀剂的缓蚀效果良好且随浓度增加而增加;两者均为混合型抑制剂,通过测试证实了金属表面上有保护膜的存在;Yadav等[9]利用合成的氨基酸化合物研究了碳钢的缓蚀性能和吸附机理,结果表明缓蚀剂类型为混合型,吸附遵循Langmuir吸附等温线;A.Kosari等[10]研究了两种吡啶衍生物在HCl溶液中停滞条件和流体动力学条件下对于低碳钢的缓蚀性能和机理;Shen Changbin等[11]研究了复合型缓蚀剂对于2024铝合金在腐蚀溶液中严重塑性变形后对电化学行为的影响,结果表明在0.2 mol/L的NaHSO3+0.6 mol/L的NaCl+0.004 mol/L Na2MoO4与0.040 mol/L的CH4N2S的溶液中,2024合金和焊缝之间的极化电阻Rp最大,抑制效率最佳.
本研究选用304不锈钢为研究对象,研究其在酸性(pH=1)3.5%氯化钠溶液中的缓蚀效率与缓蚀机理.首先,在浓度均为100 ppm条件下研究咪唑[12]、硫脲[13-14]以及铬酸钾对304不锈钢的缓蚀效果,确定最佳缓蚀剂;其次,研究任意两种复合缓蚀剂的复配对304不锈钢缓蚀效果的影响,确定最佳的复配缓蚀剂;最后研究最佳复合缓蚀剂下不同复配比例对304不锈钢缓蚀效果的影响,确定最佳复配缓蚀剂的最佳配比.
1 实验本次实验使用的是304不锈钢,材料成分如表 1所示.
| 表 1 304不锈钢(质量分数%) Table 1 Composition atomic percentage of 304 stainless steel (wt.%) |
使用Q-80Z切割机把304不锈钢切割成长约7 mm圆柱体试样,选用型号为400#、800#、1200#、2000#的砂纸进行打磨,利用P-2T金相试样抛光机进行抛光,用去离子水清洗后再用丙酮除油,之后用无水乙醇清洗.
配制100 ppm的硫脲溶液:把干燥的滤纸放在电子天平上,去皮,然后称量0.1000 g硫脲.将称量好的硫脲倒入盛有1 L、pH=1的3.5%氯化钠溶液的烧杯中,搅拌使其充分溶解.配置100 ppm的铬酸钾、咪唑溶液同上述方法.
腐蚀前用Sartorius电子天平(精确到0.001 g)称量试样;腐蚀之后去除表面腐蚀产物,冷风吹干后再称量,比较腐蚀前后的质量差值△再计算失重百分率(%).
电化学测试在普林斯顿2273电化学工作站上完成.采用标准三电极体系,工作电极为铝合金试样,辅助电极为铂片,参比电极为Ag/AgCl饱和KCl电极.电化学阻抗谱在开路电位下进行测试,频率范围为10 kHz~10 mHz,扫描速率为0.166 mV/s[15].
利用Axio Scope.A1蔡司金相显微镜和日立S3400N扫描电镜[16]对腐蚀前后的304不锈钢表面进行形貌观察.利用分析软件Proimaging对腐蚀前后的试样表面进行二值分析.
利用DSA25全自动光学法接触角测定仪在pH=1的3.5%氯化钠盐水条件下对304不锈钢进行接触角和表面张力测量,绘制溶液表面张力-浓度曲线,找到临界胶束浓度(CMC)[17],从而确定缓蚀剂最佳用量.
2 结果与分析 2.1 最佳缓蚀剂和最佳缓蚀时间的选取在室温下,将处理好的304不锈钢试样分别放入浓度为100 ppm的硫脲、铬酸钾、咪唑且pH值为1的3.5%氯化钠溶液中,静置时间分别为12、24和72 h,对304不锈钢的腐蚀速率进行测试,结果如表 2所示.
| 表 2 失重法测腐蚀速率 Table 2 Weight loss method to test the corrosion rate |
由表 2可知,三种物质及空白的腐蚀速率大小关系为:空白 > 咪唑 > 铬酸钾 > 硫脲.故可得到缓蚀效果大小关系为:硫脲 > 铬酸钾 > 咪唑 > 空白.由表 2可知在所测几组缓蚀时间下硫脲的最佳缓蚀时间是24 h, 而硫脲在这三种物质中缓蚀效果最好,所以在以下的实验中均假设最佳缓蚀时间为24 h.
图 1是添加咪唑后304不锈钢试样表面腐蚀不同时间的腐蚀形貌图.利用分析软件Proimaging对图 1中腐蚀不同时间的试样表面进行二值分析. 可知图 1中试样表面出现了明显的腐蚀现象,但24 h以后试样表面腐蚀坑的数量产生的速率渐渐降低,表明咪唑的缓蚀效果随着时间增加越来越强.

|
图 1 添加咪唑后304不锈钢在不同时间的表面腐蚀形貌 Figure 1 Surface corrosion morphology of 304 stainless steel at different time after the addition of imidazole as a corrosion inhibitor: (a) surface morphology after 12 h corrsion; (b) surface morphology after 24 h corrosion; (c) surface morphology 48 h corrosion; (d) surface morphology after 48 h corrosion |
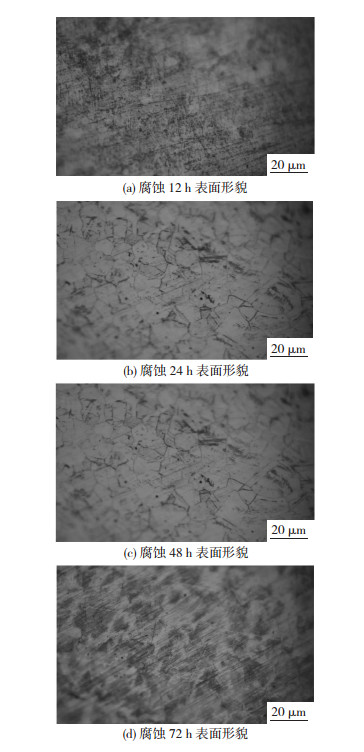
图 2为添加硫脲后304不锈钢试样表面腐蚀不同时间的腐蚀形貌图.利用分析软件Proimaging对图 2中腐蚀不同时间的试样表面进行二值分析.由图 2可知24 h以后硫脲的缓蚀效果良好,并出现随时间增加缓蚀效果逐渐增加的趋势,但在72 h以后缓蚀效果降低.
|
图 2 添加硫脲后304不锈钢在不同时间的表面腐蚀形貌 Figure 2 Surface corrosion morphology of 304 stainless steel at different time after the addition of thiourea as a corrosion inhibitor: (a) surface morphology after 12 h corrosion; (b)surface morphology after 24 h corrosion; (c) surface morphology after 48 h corrosion; (d) surface morphology after 72 h corrosion |
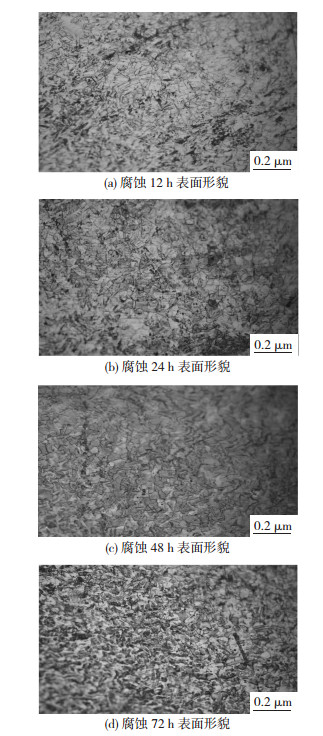
图 3为添加铬酸钾后304不锈钢试样表面腐蚀不同时间的腐蚀形貌图.利用分析软件Proimaging对图 3中腐蚀不同时间的试样表面进行二值分析.由图 3可知添加铬酸钾后其缓蚀效果不明显,但24 h后腐蚀坑数量减少72 h,具有一定的缓蚀效果.
|
图 3 添加铬酸钾后304不锈钢在不同时间的表面腐蚀形貌 Figure 3 Potassium chromate as a corrosion inhibitor 304 stainless steel in different time Surface corrosion morphology of 304 stainless steel at different tim after the addition of potassium as a corrosion inhibitor: (a) surface morphology after 12 h corrosion; (b) surface morphology after 12 h corrosion; (c) surface morphology after 48 h corrosion; (d) surface morphology after 72 h corrosion |
综上所述,由图 1~3可知添加三种物质后腐蚀时间为24 h时其缓蚀效果较好,故选择24 h作为缓蚀效果的最佳时间.
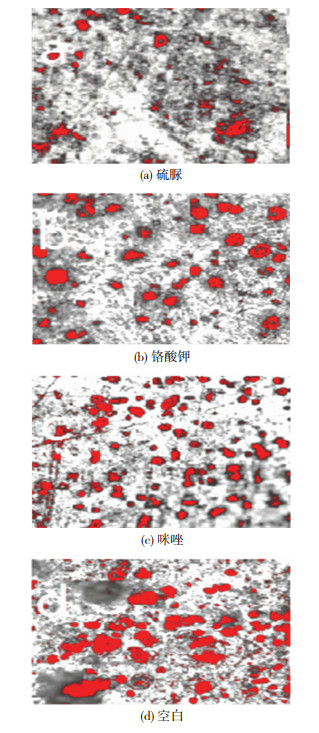
图 4为添加不同物质后304不锈钢表面的腐蚀形貌.由图 4(b)和(c)可知试样表面腐蚀坑的数量相较于(a)试样的腐蚀坑数量更少,因此硫脲和铬酸钾的缓蚀效果优于咪唑.这与失重法所得结果相一致.
|
图 4 腐蚀24 h后的二值提取图 Figure 4 Binary extraction graph after 24 h: (a) thiourea; (b) potassium; (c) imidazole; (d) blank |
比较图 4中(b)和(c)两个图,304不锈钢表面的腐蚀坑的大小和数量很难得到通过目测法得到正确的结果,因此利用二值分析法分析试样表面空隙的孔隙率可以的到想要的结果.
图 4给出了不锈钢腐蚀24 h后不同缓蚀剂条件下的二值提取图.由图 4(a)、(b)可知试样表面腐蚀坑的数量相较于(c)试样的腐蚀坑数量更少,因此硫脲和铬酸钾的缓蚀效果优于咪唑.腐蚀坑数量越少和尺寸越小表明其缓蚀效果越好,推测抗腐蚀机理可能为这三种物质通过物理或化学作用覆盖于金属表面,其厚度和均匀性决定其抗腐蚀程度.这与失重法所得结果相一致.图中腐蚀后的腐蚀坑用红色表示的,通过软件模拟分析,计算被标记部分与视场面积的面积比,测得腐蚀后的孔隙率,结果如表 3.
| 表 3 添加不同物质后的孔隙率比较 Table 3 Comparison of porosity after addition of different substances |
由表 3可知,不同添加剂孔隙率的大小关系为:咪唑 > 铬酸钾 > 硫脲.
综上所述,腐蚀时间为24 h时,100 ppm的3种缓蚀剂,硫脲的缓蚀效果优于咪唑和铬酸钾.这与失重法、表面形貌观察法所得结论相一致.
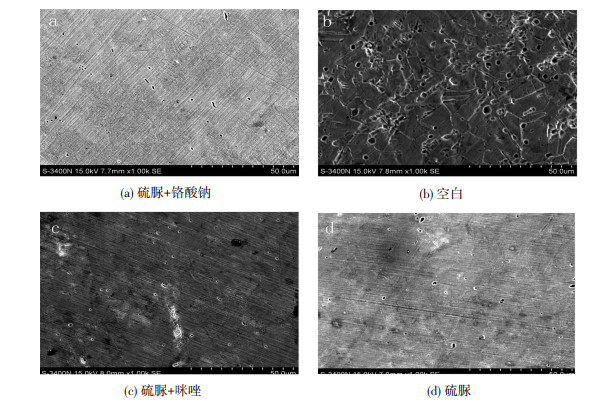
2.2 最佳复合型缓蚀剂的选择由2.1节的实验结果可知,选择硫脲为最佳缓蚀剂,故将硫脲分别与咪唑和铬酸钾按照1:1进行复配研究.在实验中用10 mL,100 ppm的硫脲分别与10 mL,100 ppm铬酸钠和咪唑进行复配,腐蚀24 h后的扫描电镜图如图 5所示.
|
图 5 缓蚀剂复配的扫描电镜图(×1 000) Figure 5 SEM scanning electron microscopy: (a) thiourea+sodium chromate; (b) blank; (c) thiourea+imidazole; (d) thiourea |
由图 5(a)、(c)可知,硫脲与铬酸钾、硫脲与咪唑进行复配,均对304不锈钢起到了很好的缓蚀效果,且硫脲+铬酸钾复配时试样表面的腐蚀坑数量明显减少;而硫脲+咪唑复配时试样表面的腐蚀坑数量虽然也有所减少,但出现少量很大的腐蚀坑.
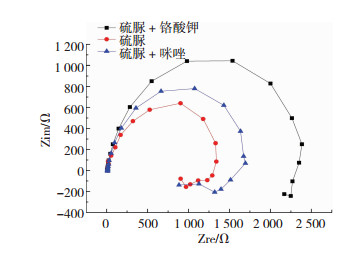
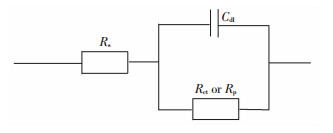
为了明确最佳缓蚀剂的复配效果,对图 5(a)和(c)两种情况进行了电化学阻抗谱的测试,结果如图 6所示. 由图 6可知,电化学阻抗谱中圆弧的半径越大,说明缓蚀剂的缓蚀效果越好[18].由此可知,缓蚀效果的大小关系为:硫脲+铬酸钾 > 硫脲+咪唑 > 硫脲.缓蚀效果最佳的复配组合是硫脲与铬酸钾.利用ZSimpWin软件进行等效电路拟合[19-20],所得结果如图 7所示.拟合电路参数如表 4所示.
|
图 6 304两种添加剂复配的电化学阻抗谱 Figure 6 Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of two kinds of additives |
|
图 7 两种添加剂复配的等效电路图 Figure 7 Equivalent circuit diagram of two kinds of additives |
| 表 4 拟合电路参数 Table 4 Fitting circuit parameters |
由表 4可知,缓蚀效果的大小关系为:硫脲+铬酸钾 > 硫脲+咪唑 > 硫脲,因此,硫脲和铬酸钾复配时其缓蚀效率最佳,可达97.4%.
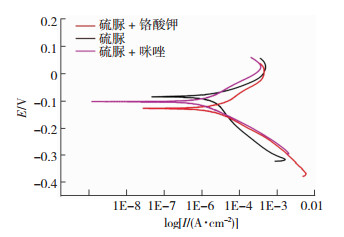
为了再次验证缓蚀效果,将硫脲+铬酸钾、硫脲+咪唑和硫脲这三种情况进行极化曲线测试,结果如图 8所示.极化曲线拟合参数如表 5所示.
|
图 8 304不锈钢的极化曲线 Figure 8 Polarization curve of 304 stainless steel |
| 表 5 304极化曲线拟合参数 Table 5 304 stainless steel polarization curve values |
由图 8可知,复配缓蚀剂与单一缓蚀剂相比自腐蚀电位均有所升高,这表明抗腐蚀能力有所提高,即复配缓蚀剂的缓蚀效果高于单一缓蚀剂的缓蚀效果.由表 5可知,腐蚀电流的大小关系为:铬酸钾+硫脲 < 咪唑+硫脲 < 硫脲,表明抗腐蚀性能的大小关系为:铬酸钾+硫脲 > 咪唑+硫脲 > 硫脲.这与表 4中缓蚀效率的结果相一致.由此可知,缓蚀剂复配的缓蚀效果高于单一缓蚀剂,且铬酸钾+硫脲的复配缓蚀效果最为明显.
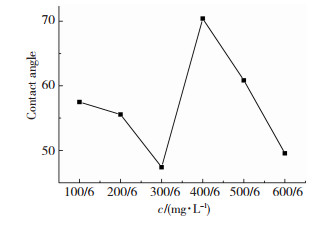
2.3 最佳复配缓蚀剂的最佳复配由上可知选择最佳复配缓蚀剂为铬酸钾与硫脲,在进行复配时,保证缓蚀剂总量固定,即总浓度均为100 ppm的情况下,使两者的复配比例分别选定为5:1,2:1,1:1,1:2,1:5.以下通过测量试样表面的接触角和表面张力的大小用以判断复配缓蚀剂的缓蚀效果.其接触角测量结果如图 9所示.利用Drop Share Analysis软件对上图的接触角进行测量,得到的结果如图 10所示.

|
图 9 不同配比下的接触角测试 Figure 9 Contact angle test under different proportions: (a) 5:1; (b) 2:1; (c) 1:1; (d) 1:2; (e) 1:5; (f) thiourea |
|
图 10 接触角随缓蚀剂配比不同的变化曲线 Figure 10 Contact angle variation with the ratio |
由图 9可知,各个配比条件下所测接触角均小于90°,可知缓蚀剂对不锈钢表面均为亲水型,即以上所有情况下均对不锈钢表面具有缓蚀作用.
由图 10可知,当复配比为1:1时其表面接触角最小,为46.5°.接触角越小表明越有利于吸附膜的形成,吸附效果越好,阻碍了腐蚀液体与金属表面的接触,从而降低了腐蚀速率.因此,当硫脲与铬酸钾复配比例为1:1时缓蚀效果最好.
图 11为表面张力随缓蚀剂不同配比(5:1、2:1、1:1、1:2、1:5)的变化关系. 由图 11可知当复配比为1:1时不锈钢的表面张力最小,为71.9 mN/m,复配的缓蚀效果最好.原因为表面张力越小使得金属表面对缓蚀剂的吸附越容易,这样溶液和金属之间的界面越容易改变,使得金属表面能降低,腐蚀体系所需的活化能增加,使得腐蚀反应更难进行[21].

|
图 11 表面张力随缓蚀剂不同配比中硫脲浓度的变化关系 Figure 11 Relationship between surface tension and thiourea concentration in different proportion of corrosion inhibitor |
1) 咪唑、硫脲、铬酸钾这3种物质均对304不锈钢在酸性腐蚀溶液中具有一定的缓蚀效果;缓蚀效率大小关系为:硫脲 > 铬酸钾 > 咪唑.因此,在现有实验条件下选择硫脲作为最佳缓蚀剂.
2) 通过金相观察、电化学阻抗谱、极化曲线测试均表明硫脲与铬酸钾复配的缓蚀效果最好.因此,在现有实验条件下最佳的缓蚀剂复配为硫脲与铬酸钾.
3) 通过表面接触角和表面张力的结果均表明硫脲与铬酸钾配比为1:1时其缓蚀效果最佳.因此,在现有实验条件下缓蚀剂的最佳配比为1:1.
| [1] | K H, SHEK C H, LAI J K L. Rencent development instainless steels[J]. Materials Science & Engineering R, 2009, 65(4-6): 39–42. |
| [2] | XING Xuegang, HAN Zhijun, WANG Hefeng, et al. Electrochemical corrosion resistance of CeO2-Cr/Ti coatings on 304 stainless steel via pack cementation[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2015, 10: 1002–0721. |
| [3] | ILEVBARE G O, BURSTEIN G T. The inhibition of pitting corrosion of stainless steels by chromate and molybdate ions[J]. Corrosion Science, 2003: 1545–1569. |
| [4] | TIAN Wenming, DU Nan, LI Songmei, et al. Metastable pitting corrosion of 304 stainless steel in 3.5% NaCl solution[J]. Corrosion Science, 2014, 85: 372. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2014.04.033 |
| [5] | LI Yang, ZHANG Shangzhou, HE Yongyong, et al. Characteristics of the nitrided layer formed on AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel by high temperature nitriding assisted hollow cathode discharge[J]. Materials & Design, 2014, 64: 527. |
| [6] | ALBRIMI Y A, ADDI A A, DOUCH J, et al. Inhibition of the pitting corrosion of 304 stainless steel in 0.5 M hydrochloric acid solution by heptamolybdate ions[J]. Corrosion Science, 2015, 90: 522. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2014.10.023 |
| [7] | SUN Caixia, XU Huiwu, CHEN Yanmin, et al. Research of corrosion inhibitor composed by sodium molybdate[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2013, 42(9): 1608–1613. |
| [8] | ZAKARIA K, HAMDY A, ABBAS M A, et al. New organic compounds based on siloxane moiety as corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel in HCl solution: weight loss, electrochemical and surface studies[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2016, 65: 530–543. DOI: 10.1016/j.jtice.2016.05.036 |
| [9] | YADAV M, GOPE L, SARKAR T K. Synthesized amino acid compounds as eco-friendly corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution: electrochemical and quantum studies[J]. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 2016, 42(3): 2641–2660. DOI: 10.1007/s11164-015-2172-5 |
| [10] | KOSARI A, MOAYED M H, DAVOODI A. Electrochemical and quantum chemical assessment of two organic compounds from pyridine derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in HCl solution under stagnant condition and hydrodynamic flow[J]. Corrosion Science, 2014, 78: 138–150. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2013.09.009 |
| [11] | SHEN Changbin, YANG Ye, GE Jingping. Effect of compounded inhibitor on the electrochemical behaviour of 2024 aluminum alloy after severe plastic deformation in the ambient corrosive aquous solution[J]. Rare Metal Materialsand Engineering, 2013, 42(2): 529–532. |
| [12] | YAN Qianru, MA Yangmin, YANG Xiufang, et al. Synthesis and performance of imidazoline corrosion inhibitor from platycladus orientalis seed oil[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry College, 2013, 130: 133, 226. |
| [13] | FUJIMON T, NAKAMURA M, TAKAOKA M, et al. Synergetic inhibition of thermochemical formation of chlorinated aromatics by sulfur and nitrogen from thiourea: multielement characterization[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016. 02. 054. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304389416301819 |
| [14] | SHANKARAIAH N, KUMAR P N, AMULA B S. One-pot synthesis of podophyllotoxin-thiourea congeners by employing NH2SO3H/Nal:anticancer activity, DNA topoisomerase-ll inhibitor, and apoptosis inducing agents[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2015, 25(19): 4239–4244. |
| [15] | BENTISS F, TRAISNEL M. Inhibitor effects of triazole derivatives on corrosion of mild steel in acidic media[J]. British Corrosion Journal, 2000, 34(4): 315–320. |
| [16] |
寇沙沙, 李智丽, 靳燕. 扫描电镜在金属材料检测的应用[J]. 包钢科技, 2016.01.012. KOU Shasha, LI Zhili, JIN Yan. Application of scanning electron microscopy in metallic materials[J]. Baogang Technology, 2016.01.012. DOI: 10.1364/j.cnki.btgkj.2016.01.012 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=BGKJ201601014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ |
| [17] | WANG Yishan. Adsorption and corrosion inhibition of several organic inhibitors on carbon steel in simulated concrete pore solution[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2016. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40735-016-0052-1 |
| [18] | CARDONA C, TORRES A A. Assessment of dimethyl benzodiimidazoles as corrosion inhibitor of austenitic stainless steel grade 316L in acid medium[J]. Electrochemistry Science, 2015, 10: 1966–1978. |
| [19] | ELSENER B, ADDARI D, CORAY S. Nickel-free manganese bearing stainless steel in alkaline media-elecrochemistry and surface chemistry[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(12): 4489–4497. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2011.02.049 |
| [20] | BETOVA I, BOJINOV M, KINNUNEN P, et al. Surface film electrochemistry of austerities stainless steel and its main constituents in supercritical water[J]. Jsupflu. 2007.06.005. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0896844607002422 |
| [21] | SOUZA R P, FERRARI V J, GUEDES C I. Low toxic polymeric surfactant as a corrosioninhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric acid medium[J]. Emerald, ACMM-01-2015-1485 http://www.emeraldinsight.com/doi/full/10.1108/ACMM-11-2014-1458 |
 2018, Vol. 26
2018, Vol. 26


