研究目的:探究纳米颗粒对鼓泡塔氨法吸收二氧化碳的强化作用
研究方法:
(1)试剂:氨水,质量分数为25%-28%,天津化工有限公司生产;二氧化碳气体,纯度为99.99%,氮气,99.99%,保定北方特种气体有限公司生产;纳米颗粒(SiO2、TiO2、CuO),由南京埃普瑞纳米材料有限公司提供。
(2)本文纳米流体的制备方法采用的是“两步法”,首先用天平准确称取所需的纳米TiO2、CuO、SiO2,量取所需要的蒸馏水,然后通过机械分散20分钟,加入一定量的氨水,继续机械分散10分钟制备为不同质量分数的纳米流体,纳米流体的分散稳定性良好。
(3)实验系统:纳米颗粒强化氨水鼓泡吸收CO2实验系统如图所示,主要包括鼓泡吸收塔、烟气配送系统、尾气测量处理系统。
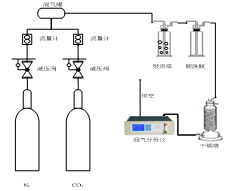
实验步骤:
(1)实验前先计算出配制纳米流体所需的纳米颗粒、氨水、蒸馏水的量,用电子秤称出纳米颗粒的质量,将其加入到蒸馏水中,机械搅拌20min,加入一定量的氨水,继续机械分散10分钟制备为不同质量分数的纳米流体;
(2)打开分析仪预热30min,开通N2对整个系统进行吹扫,待CO2烟气分析仪示数降为0时。按照比例将氮气与二氧化碳充入混合瓶,混合均匀后通入分析仪,待示数达到预设值且稳定;
(3)将配制好的纳米流体加入到反应塔内,开始计数,每5s计数一次,待示数不再降低,停止计数。
为减少偶然误差带来的影响,每组实验均进行5次,然后取其平均值。为减少氨水浓度对本实验的影响,每次实验都要测量配制好的溶液的pH值,保证初始溶液具有相同pH值。
结果:
(1)纳米颗粒种类和固含量对增强因子的影响
对氨水质量分数为1%,CuO、TiO2、SiO2颗粒添加量分别为1g/L、2g/L、3g/L、4g/L、5g/L的纳米流体进行鼓泡吸收实验,增强因子如图所示:

增强因子与纳米颗粒种类的关系
从图中可以看到只有添加TiO2这一种纳米颗粒时,其增强因子一直大于1;添加SiO2 纳米颗粒,只有在1g/L、2g/L时,增强因子略大于1,其他添加量则小于1;添加CuO 纳米颗粒,其增强因子始终在1左右徘徊,没有出现出明显的增强或抑制作用。
(2) 氨水浓度对增强因子的影响
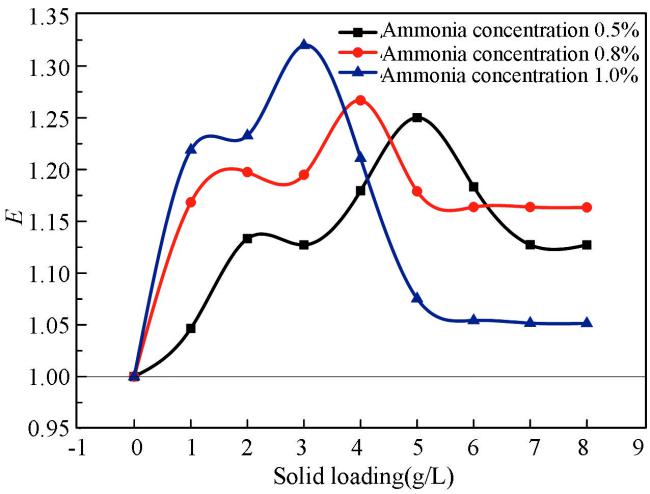
从图中可以看出,不同氨水浓度下,增强因子的变化趋势随固含量的增加先升高后降低。但是,它们的最佳固含量不同,随着氨水浓度的升高,最佳固含量降低。
(3) 纳米颗粒种类对脱除率的影响
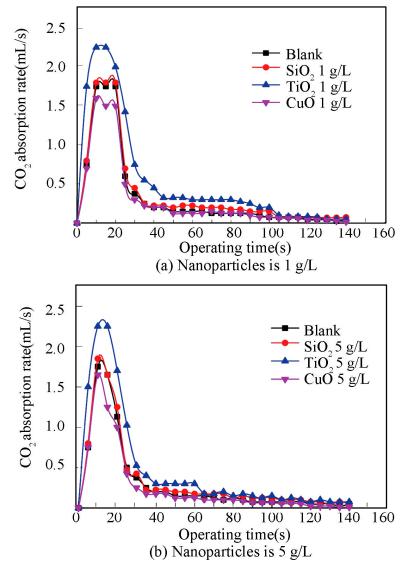
从图中可以看出,TiO2纳米流体的吸收率要大于空白溶液,CuO纳米流体的吸收率和空白溶液相同,而SiO2纳米流体的吸收率小于空白溶液。
(4)纳米颗粒添加量对脱除率的影响
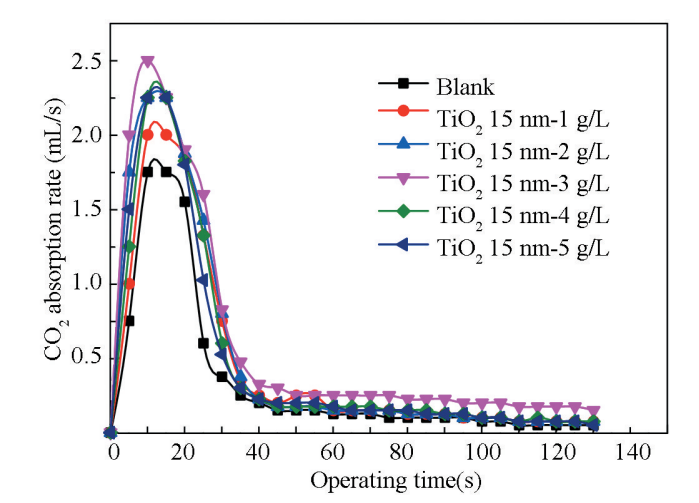
从图中可以看出,脱除率随纳米颗粒添加量的增加先增高后降低,且脱除率一直大于空白溶液实验,在纳米颗粒添加量为3.0g/L时脱除率达到最大值。
结论:
(1)纳米颗粒的添加对于部分有化学反应气液传质过程具有强化作用,其强化作用与纳米颗粒和溶剂的性质有关;
(2)对气体溶质具有选择吸附性、增溶剂性的纳米颗粒可对有化学反应的气液传质过程有强化作用。其强化作用随着纳米颗粒添加量的增加先增大后减小,即纳米TiO2的含量对强化氨水捕集CO2存在一个最佳固含量;
(3)对气体溶质没有吸附性但具有亲溶剂性的纳米颗粒可对有化学反应的气液传质过程有抑制作用。其抑制作用随着纳米颗粒添加量的增加而逐渐增强;
(4)纳米颗粒强化有化学反应的气液传质过程的机理可总结为,纳米颗粒在布朗运动的作用下会使吸收工质内部形成微对流,从而使分子扩散系数增大。纳米颗粒对气体溶质的吸附性,使传质边界层内气相溶质浓度降低,传质边界层内的浓度梯度增大,传质推动力增加,气体吸收得到强化。
关键词:纳米颗粒;鼓泡塔吸收;氨水;CO2捕集;强化吸收









