摘要
为研究冷弯薄壁型钢材料在高温和锈蚀耦合作用下力学性能变化规律,通过中性盐雾锈蚀、高温煅烧、冷却和拉伸试验,对 180 个经历 0 ~ 60 d 人工加速锈蚀和 20 ~ 800 ℃高温煅烧后 1. 5 mm 厚 S280GD + Z 型冷轧薄钢板在自然冷却和浸水冷却方式下的力学性能进行了试验研究。结果表明:在锈蚀和高温耦合作用下,钢材表面特征和破坏模式受冷却方式影响较大;锈蚀率小于 6% 时,锈蚀对 S280GD + Z 钢材力学性能影响较小;受火温度低于 600 ℃时,受火温度及冷却方式对 S280GD + Z 钢材屈服强度、极限强度影响不显著;在锈蚀和高温耦合作用下,受火温度大于 600 ℃ 后,钢材强度退化幅度变大并且高温在对钢材强度影响中占主导地位;冷却方式对钢材伸长率影响较大,自然冷却条件下,伸长率随受火温度呈先增加后减小趋势,浸水冷却条件下,伸长率随受火温度整体呈降低趋势。建立了锈蚀与高温耦合作用下,S280GD + Z 钢材力学参数与锈蚀率、受火温度之间定量关系的数学模型,基于简化的二次塑流模型建立了锈蚀与高温耦合作用下 S280GD + Z 钢材本构模型。
Abstract
In order to study the variation of mechanical properties of cold-formed thin-walled steel materials under the coupling effect of high temperature and corrosion, a series of experiments involving neutral salt spray corrosion, high-temperature calcination, cooling and tensile tests were conducted. The mechanical properties of 180 S280GD + Z cold-rolled steel sheets with thickness of 1. 5 mm, which underwent accelerated corrosion for 0-60 d and high temperature calcination from 20 to 800 ℃ , were studied under cooling in air and cooling in water. The results indicate that under the coupling effect of corrosion and high temperature, the surface characteristics and failure modes of the steel are greatly affected by the cooling methods. When the corrosion rate is less than 6% , the corrosion has little impact on the mechanical properties of S280GD + Z steel. When the fire temperature is below 600 ℃ , the fire temperature and cooling methods have insignificant effects on the yield strength and ultimate strength of S280GD + Z steel. However, under the coupling effect of corrosion and high temperature, when the fire temperature exceeds 600 ℃ , the strength degradation of steel becomes the dominant factor affecting the strength of steel. The cooling method has a significant impact on the elongation of the steel. Under natural cooling conditions, the elongation increases and then decreases with the increase in fire temperature. Under immersion cooling conditions, the elongation shows an overall decreasing trend with the increase in fire temperature. A mathematical model was established to quantify relationship between the mechanical parameters of S280GD + Z steel and the corrosion rate and temperature under the coupling effect of corrosion and high temperature. Based on a simplified secondary plastic flow model, a constitutive model for S280GD + Z steel under the coupling effect of corrosion and high temperature was established.
冷弯薄壁型钢结构具有材料回收率高、自重轻、抗震性能优异、易于施工等一系列优点[1-2],已在房屋建筑、轻型桁架厂房、仓储式货架、太阳能光伏支架等众多领域广泛应用。然而受限于钢材耐腐蚀性和耐高温性不良等因素,冷弯薄壁型钢结构长期服役过程的安全性问题逐渐凸显,并成为困扰其推广使用的核心因素之一。
近年来,学者们围绕冷弯薄壁型钢材锈蚀[3-7] 和高温[8-11] 后性能开展了大量研究工作。文献[3-7]通过工业环境下服役 9 年的冷弯薄壁 C 型檩条拉伸试验发现,锈蚀对冷成型钢材性能影响高于热轧型钢[3],并且锈蚀加剧了冷弯效应对钢材强度和延展性的影响[4-5],随着锈蚀程度增加,钢材屈服强度和极限强度、极限应变、弹性模量呈线性下降趋势,伸长率呈二次下降趋势[6]。文献[7] 研究了钢材断口形态与锈蚀程度之间的关系,并建立了锈损冷弯薄壁型钢本构模型。文献[8-10]重点考察了受火温度、冷却方式、加热模式等因素对屈服强度、极限强度、弹性模量、极限应变、伸长率、受拉本构模型等指标的影响,研究表明,冷成型钢材性能在浸水冷却与自然冷却方式下差异较大,浸水冷却方式下,冷成型钢材屈服强度和极限强度随受火温度提高而增大,伸长率和极限应变随受火温度提高而降低[8],随着受火温度提高,冷成型钢材力学性能总体上呈现下降趋势,受火温度存在临界值(500℃ 左右),低于临界值时,屈服强度、极限强度、伸长率和极限应变随受火温度提高小幅波动,高于临界值后,屈服强度和极限强度随受火温度提高明显降低,伸长率和极限应变随受火温度提高而增大[9-10]。弹性模量受煅烧温度和冷却方式影响较小[10]。
综上可知,现阶段围绕冷弯薄壁型钢材高温和锈蚀后性能的研究大多仅考虑高温或锈蚀单独作用,事实上火灾往往发生在结构服役过程中,钢材受到高温和锈蚀双重作用,然而目前鲜见冷弯薄壁型钢材在高温和锈蚀耦合作用下的研究报道。基于此,以 1.5 mm 厚 S280GD + Z 型冷轧薄钢为研究对象,通过人工加速锈蚀、高温煅烧、冷却和拉伸试验,分析其力学性能变化规律,建立了力学性能与锈蚀程度、煅烧温度之间关系的数学模型以及锈蚀和高温耦合作用下的单轴受拉本构模型,为冷弯薄壁结构抗火设计与加固理论提供参考。
1 试验
1.1 试件设计
所有试件采用 S280GD + Z 型冷轧薄钢板通过线切割方式截取。参考 GB / T228.1—2021《金属材料拉伸试验第 1 部分:室温试验方法》 [11],试件截面设计为矩形,尺寸如图1所示,厚度为 1.5 mm。锈蚀龄期为 0(对照组)、3、10、30、45、60 d,受火温度分别为 20(常温)、300、600、700、800℃,冷却方式包括自然冷却和浸水冷却。根据试件锈蚀龄期、受火温度和冷却方式,共设计 60 组试件,每组 3 个,共计 180 个。试件编号规则如图2所示。
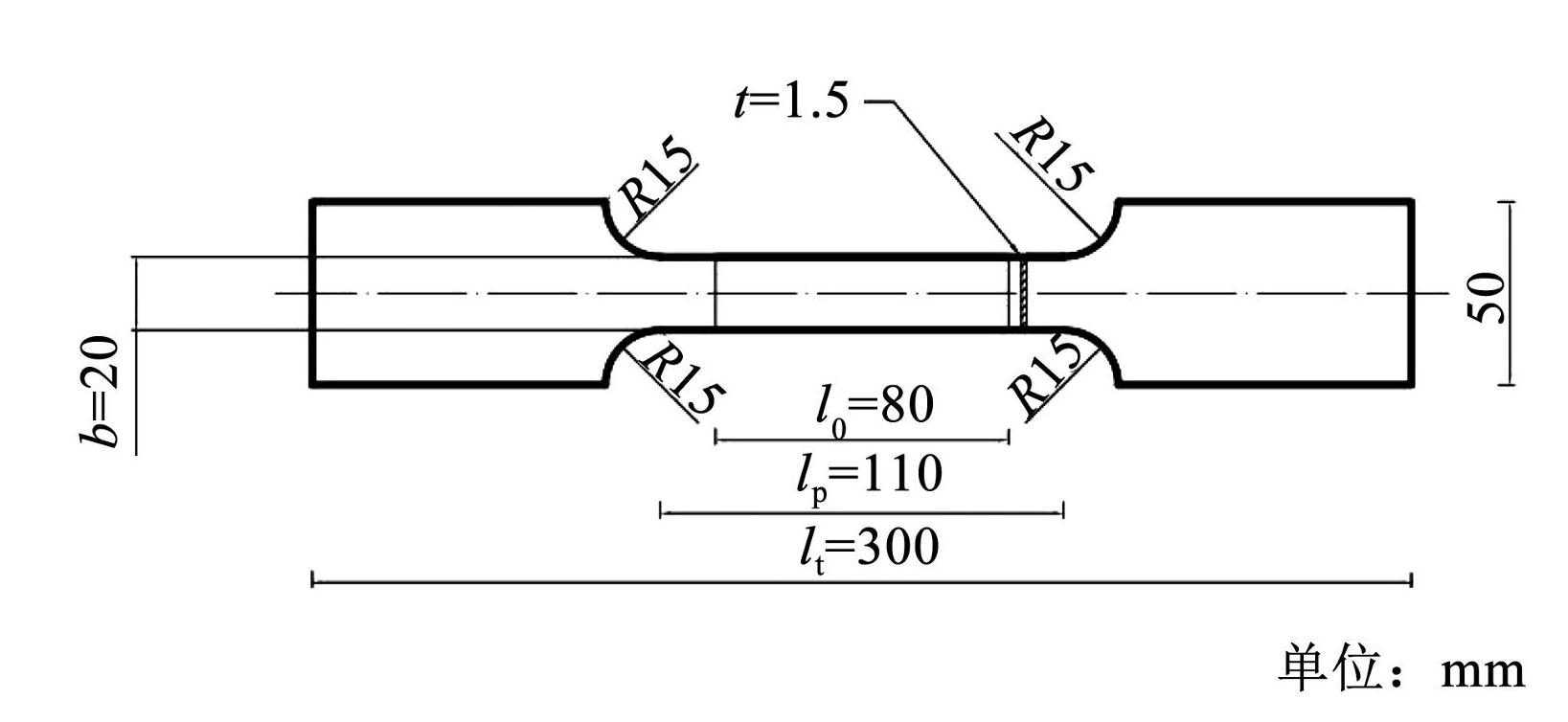
图1试件几何尺寸
Fig.1Geometry of specimens
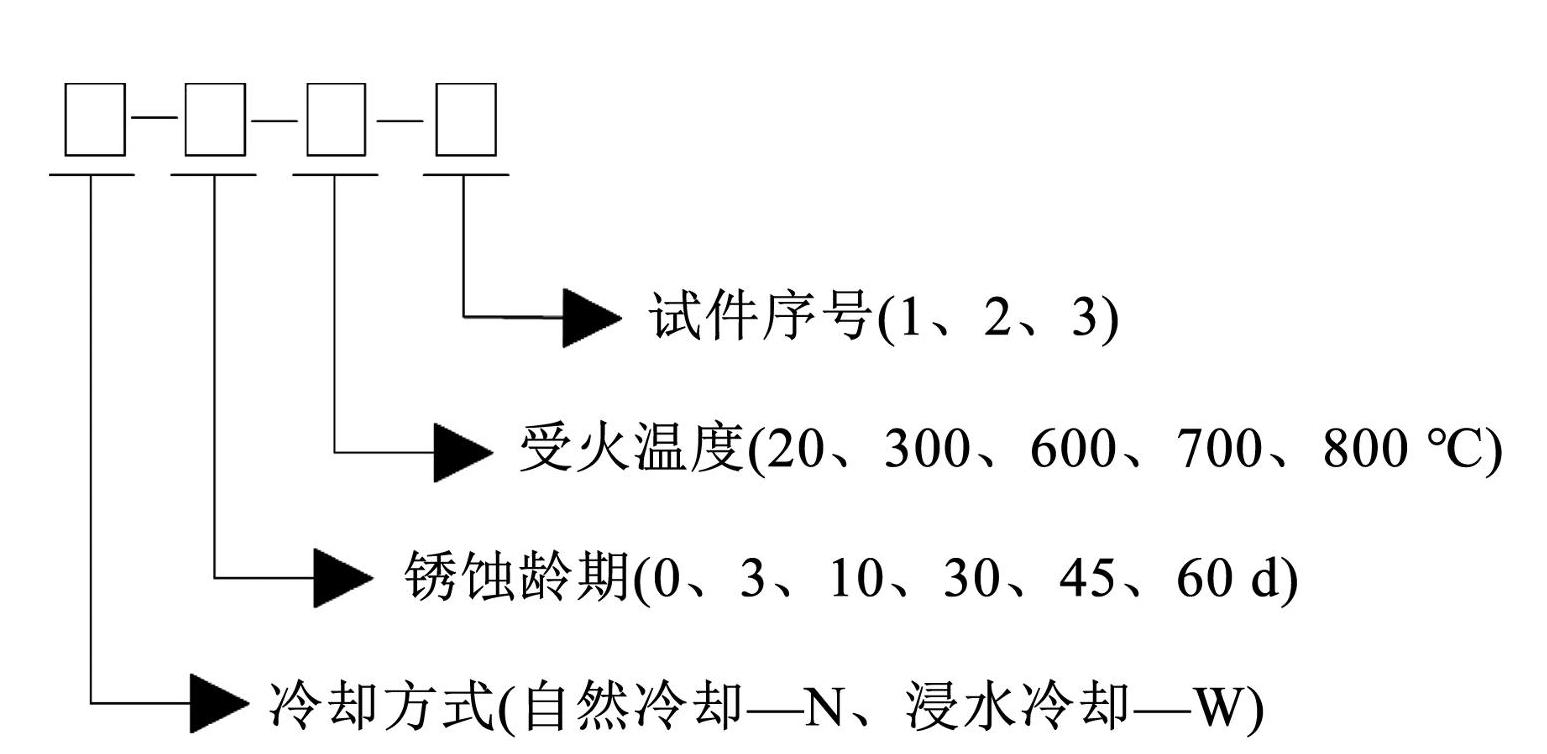
图2试件编号规则
Fig.2Specimen numbering rules
1.2 试验方案
本试验主要包括 4 部分,即中性盐雾锈蚀、高温煅烧、冷却和室温单调拉伸。
中性盐雾试验采用精密型盐雾试验机,高温煅烧采用 HDX 高温热电炉,升温速率为 10℃ / min,高温试件采用自然冷却和浸水冷却两种方式,室温拉伸试验采用 WDW3030 微控电子万能试验机,最大荷载为 30 kN。
1)根据 GB / T10125—2021 《人造气氛腐蚀试验盐雾试验》 [12],制定锈蚀试验方案。采用质量损失率表征试件锈蚀率,将锈蚀完成试件取样后除锈、烘干,称量质量并计算质量损失率。
2)将锈蚀完成试件放入 HDX 高温热电炉内,以 10℃ / min 速率升温,达到预设温度后保温 20 min,随后取出冷却。
3)将冷却后试件在室温条件下放置 2 d,然后进行单调拉伸试验。
4)拉伸试验依据 GB / T228.1—2021《金属材料拉伸试验第 1 部分:室温试验方法》 [11]进行,加载采用位移控制,加载速率为 2 mm / min,试验力通过试验机自动采集,变形通过电子千分表自动采集,取 3 个试件的平均值作为每组试件最终结果。
2 试验结果与讨论
2.1 试验现象
不同锈蚀龄期 S280GD + Z 钢材试件高温煅烧后表面特征和破坏模式如图3所示。可以看出,随着锈蚀龄期增加,试件表面氧化物增多,颜色逐渐变深。锈蚀龄期大于 45 d 后,不同受火温度试件表面颜色相差不大,均比未锈蚀试件表面颜色深,可能主要还是锈蚀破坏钢材镀锌层导致。受火温度高于 600℃ 后,试件表面颜色明显变深,随着温度升高,试件表面颜色逐渐加深变黑,甚至出现表皮剥离脱落,尤其是浸水冷却试件表皮剥落更为严重。受火温度高于 700℃时,试件铁锈完全脱落,试件明显变薄; 自然冷却下试件断口会表现出紧缩现象,而浸水冷却试件多为斜向平整断口; 温度高于 600℃时,浸水冷却试件会发生严重变形,表现为试件变短。

图3不同锈蚀龄期试件表面特征和破坏模式
Fig.3Surface characteristics and failure modes of test specimens with different corrosion ages
2.2 锈蚀率
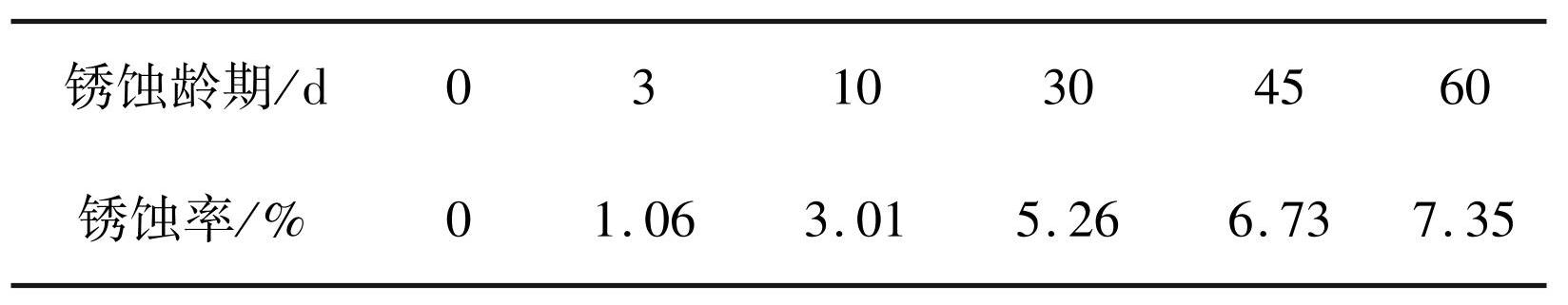
不同锈蚀龄期锈蚀率如表1所示。可以看出,随着锈蚀龄期增加,锈蚀率逐渐增大。但由于设备的局限性,单位时间内各试件表面接触到的盐雾量不可能完全相同,导致相同锈蚀龄期试件之间锈蚀率也有差异,但波动不大。随着锈蚀龄期增加,试件锈蚀速率放缓,由于锈蚀产物层变厚,对试件表面起到了保护作用。
表1锈蚀率
Tab.1 Corrosion rate
通常,针对碳钢、低合金钢的腐蚀速率模型有幂函数和指数形式模型、灰色 GM 模型、考虑大气成分腐蚀模型等[13-14]。综合考虑以上几种模型优缺点,选用幂函数模型对 S280GD + Z 钢材锈蚀率与锈蚀龄期间关系进行拟合分析。所建立锈蚀率与锈蚀龄期关系如图4所示,拟合公式如下:
(1)
式中:η 为锈蚀质量损失率,%; d 为锈蚀龄期,d。
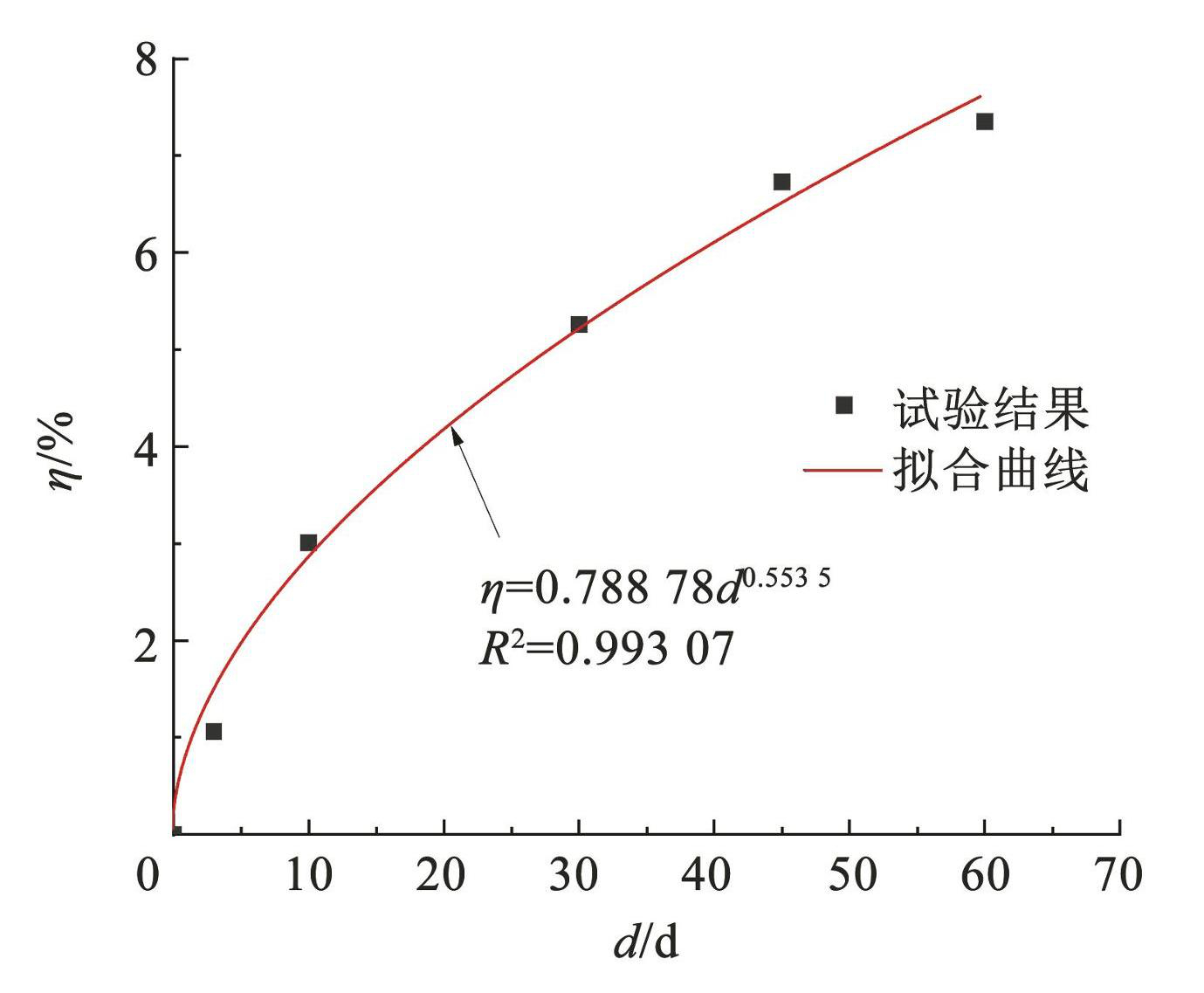
图4锈蚀率与锈蚀龄期关系曲线
Fig.4Relationship curve between corrosion rate and corrosion age
2.3 应力-应变曲线
不同锈蚀龄期 S280GD + Z 钢材高温冷却后应力-应变曲线如图5所示。可以看出:不同锈蚀龄期、受火温度和冷却方式下的应力-应变曲线形状基本类似,除 W-60-800 试件外,其余试件均可分为 4 个阶段,即弹性阶段、屈服阶段、塑性阶段和应力强化阶段; W-60-800 试件未出现明显屈服平台,主要可能是锈蚀 60 d 试件浸水冷却后表皮大量脱落,试件太薄导致高温后发生严重变形,进而影响塑性变形能力; 常温下,随着锈蚀龄期增加,钢材极限拉应变变化不明显; 自然冷却方式下,除锈蚀 60 d 试件外,随着受火温度增加,钢材极限抗拉应变变化不大; 浸水冷却条件下,受火温度低于 600℃ 时,钢材极限拉应变受受火温度影响较小,受火温度高于 600℃时,随着受火温度提高,钢材极限拉应变显著降低。

图5不同锈蚀龄期钢材高温冷却后应力-应变曲线
Fig.5Stress-strain curves of steel with different corrosion ages after cooling from high temperature
2.4 力学参数
不同冷却方式和锈蚀龄期 S280GD + Z 钢材力学参数及折减系数如表2所示。为了描述高温、锈蚀和冷却方式对 S280GD + Z 钢材各力学性能参数的影响,引入折减系数。折减系数为高温后锈蚀试件力学参数与常温条件下未锈蚀试件力学参数比值。 f y,t,d为锈蚀 d d 煅烧 t 温度后试件屈服强度,f为常温条件下未锈蚀试件屈服强度,f u,t,d为锈蚀 d d 煅烧 t 温度后试件极限强度,f u为常温条件下未锈蚀试件极限强度,Et,d为锈蚀 d d 煅烧 t 温度后试件弹性模量,E 为常温条件下未锈蚀试件弹性模量,At,d 为锈蚀 d d 煅烧 t 温度后试件伸长率,A 为常温条件下未锈蚀试件伸长率。
表2不同冷却方式下锈蚀 S280GD + Z 钢材高温后力学参数及折减系数
Tab.2 Mechanical parameters and reduction factors of corroded S280GD + Z steel after high-temperature with different cooling methods

2.4.1 屈服强度
不同锈蚀龄期 S280GD + Z 钢材在不同冷却方式下屈服强度折减系数随受火温度变化规律如图6所示。钢材应力-应变曲线具有明显屈服平台的,取屈服平台下屈服应力作为试件屈服强度,没有明显屈服平台的,取产生 0.2% 变形的应力值为屈服强度。不论是自然冷却还是浸水冷却,受火温度低于 600℃ 时,锈蚀龄期对钢材屈服强度影响较小(不超过 5%)。受火温度大于 600℃ 后,随着受火温度提高,自然冷却下钢材屈服强度显著降低,浸水冷却下钢材屈服强度显著增大。自然冷却条件下,未锈蚀试件经 800℃ 高温煅烧后屈服强度降低20 %,而锈蚀 3、10、30、45、60 d 试件经 800℃ 高温煅烧后屈服强度分别降低 23%、25%、25%、25% 和 25%,由此可知,在锈蚀和高温耦合作用下,温度对钢材屈服强度的影响占主导地位,并且锈蚀对钢材屈服强度的影响随受火温度的升高而降低; 浸水冷却条件下,未锈蚀试件经 800℃ 高温煅烧后屈服强度提高 27%,锈蚀 3、10、30、45、60 d 试件则分别提高 25%、24%、26%、30% 和 15%,说明浸水冷却方式下,当锈蚀龄期小于 45 d 时,锈蚀程度对钢材屈服强度的影响不明显,锈蚀龄期达到 60 d 时,屈服强度增幅明显降低,这可能与试件过薄导致的高温后变形较大有关。
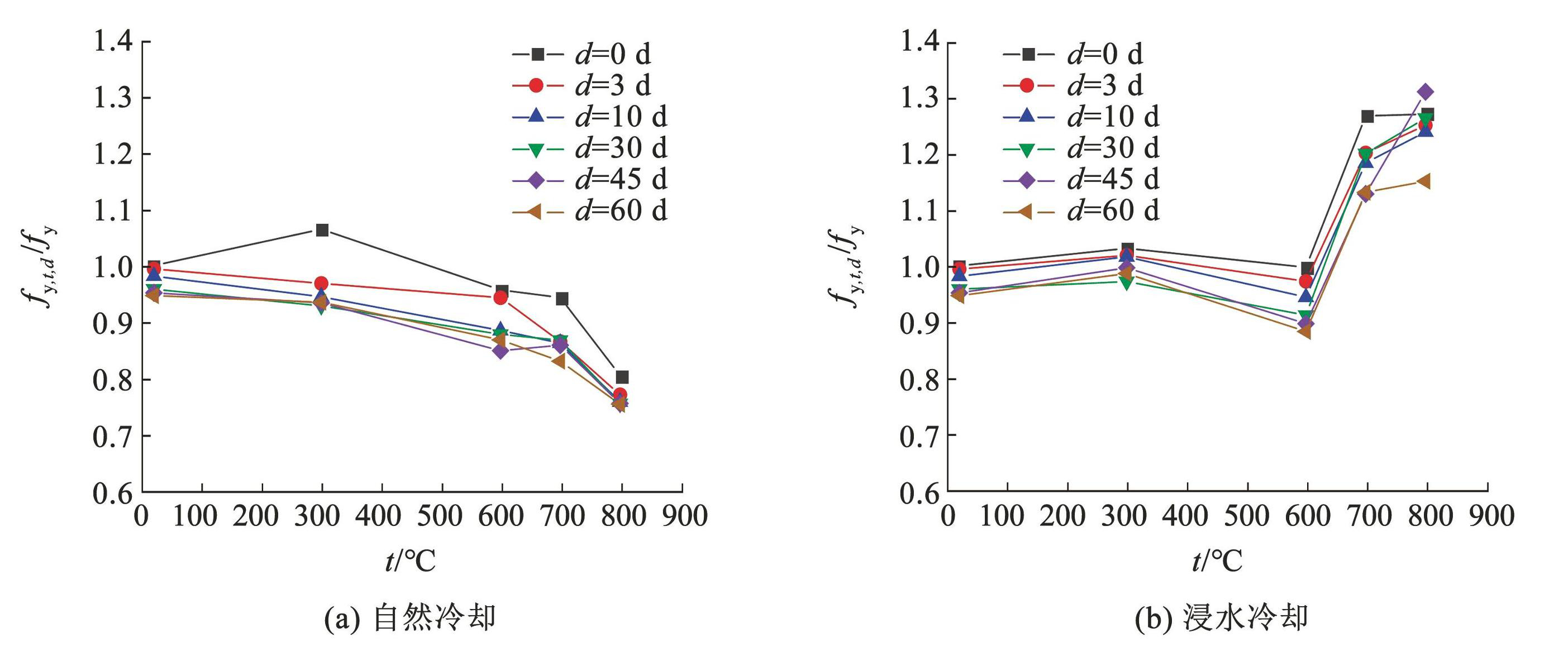
图6不同锈蚀龄期钢材高温冷却后屈服强度变化
Fig.6Yield strength variation of steel at different corrosion ages after high-temperature cooling
2.4.2 极限强度
不同锈蚀龄期 S280GD + Z 钢材在不同冷却方式下极限强度折减系数随受火温度变化如图7所示。可以看出:自然冷却条件下,钢材极限强度随着温度升高和锈蚀龄期增加逐渐降低; 未锈蚀试件经 800℃ 高温煅烧后极限强度降低 17%,而经历 800℃煅烧后,锈蚀 60 d 试件经 800℃ 高温煅烧后极限强度降低 26%,说明在锈蚀和高温耦合作用下,钢材极限强度退化速度加快。浸水冷却条件下,钢材极限强度随受火温度的升高先小幅波动再显著升高,拐点为 600℃ 左右,受火温度由 600℃ 升至 800℃时,钢材经 0、3、10、30、45、60 d 锈蚀后极限强度分别提升 26%、25%、30%、31%、41% 和 30%,表明锈蚀后的冷成型钢材淬火效应更加明显,表现为极限强度增幅更大。

图7不同锈蚀龄期钢材高温冷却后极限强度变化
Fig.7Variation of ultimate strength of steel with different corrosion ages after high-temperature cooling
2.4.3 弹性模量
不同锈蚀龄期 S280GD + Z 钢材在不同冷却方式下弹性模量折减系数随受火温度变化如图8所示。可以看出,S280GD + Z 钢材弹性模量受冷却方式影响较小。随着受火温度提高,弹性模量变化较小,不超过 4%; 随着锈蚀龄期增加,钢材弹性模量最大降低 5%; 在锈蚀和高温耦合作用下,弹性模量降低幅度不超过 6%。说明高温和锈蚀对 S280GD + Z 钢材弹性模量影响较小,可以忽略不计。
2.4.4 伸长率
不同锈蚀龄期 S280GD + Z 钢材在不同冷却方式下伸长率折减系数随受火温度变化如图9所示。可以看出,不论是自然冷却还是浸水冷却,同一受火温度时,伸长率随着锈蚀龄期增加而降低。自然冷却条件下,锈蚀龄期在 30 d 之内时,伸长率随温度升高呈上下小幅波动趋势,锈蚀龄期为 45 d 和 60 d 时,伸长率随温度呈先增加后减小趋势,峰值出现在 600℃左右; 在锈蚀和高温耦合作用下,伸长率最大降幅出现在受火温度 800℃和锈蚀龄期 60 d 时,降幅达 43%。浸水冷却条件下,伸长率随受火温度整体呈降低趋势,并在 600~700℃ 时急剧降低,平均降幅在 20% 以上,在 700~800℃ 时伸长率变化趋于平缓; 在锈蚀和高温耦合作用下,伸长率最高降幅出现在受火温度 800℃和锈蚀龄期 60 d 时,降幅达71 %。表明锈蚀和高温耦合作用将使得冷成型钢材脆性进一步增大。
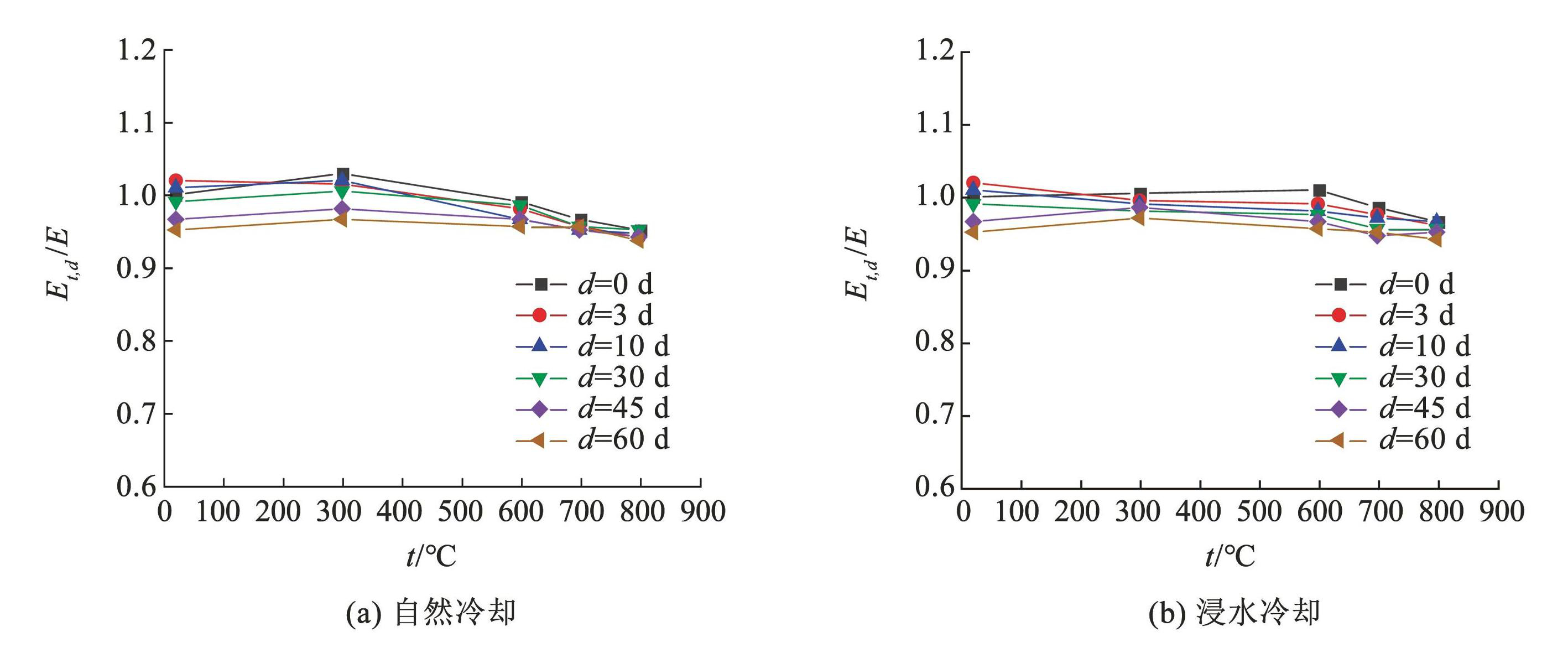
图8不同锈蚀龄期钢材高温冷却后弹性模量变化规律
Fig.8Variation of elastic modulus of steel with different corrosion ages after high-temperature cooling

图9不同锈蚀龄期钢材高温冷却后伸长率变化
Fig.9Variation of elongation of steel with different corrosion ages after high-temperature cooling
3 拟合公式
上述分析可知,S280GD + Z 钢材在锈蚀和高温的耦合作用下力学性能变化较复杂。为更好地描述 S280GD + Z 钢材在锈蚀和高温耦合作用下的力学性能退化规律,采用 Levenberg-Marquardt 算法对本文试验结果进行二元非线性拟合分析,建立不同锈蚀程度试件在不同冷却方式下屈服强度、极限强度和伸长率数学模型。试验结果与数学模型对比见图10~12。

图10屈服强度折减系数试验结果与数学模型对比
Fig.10Comparison of test results and mathematical model of yield strength reduction factors
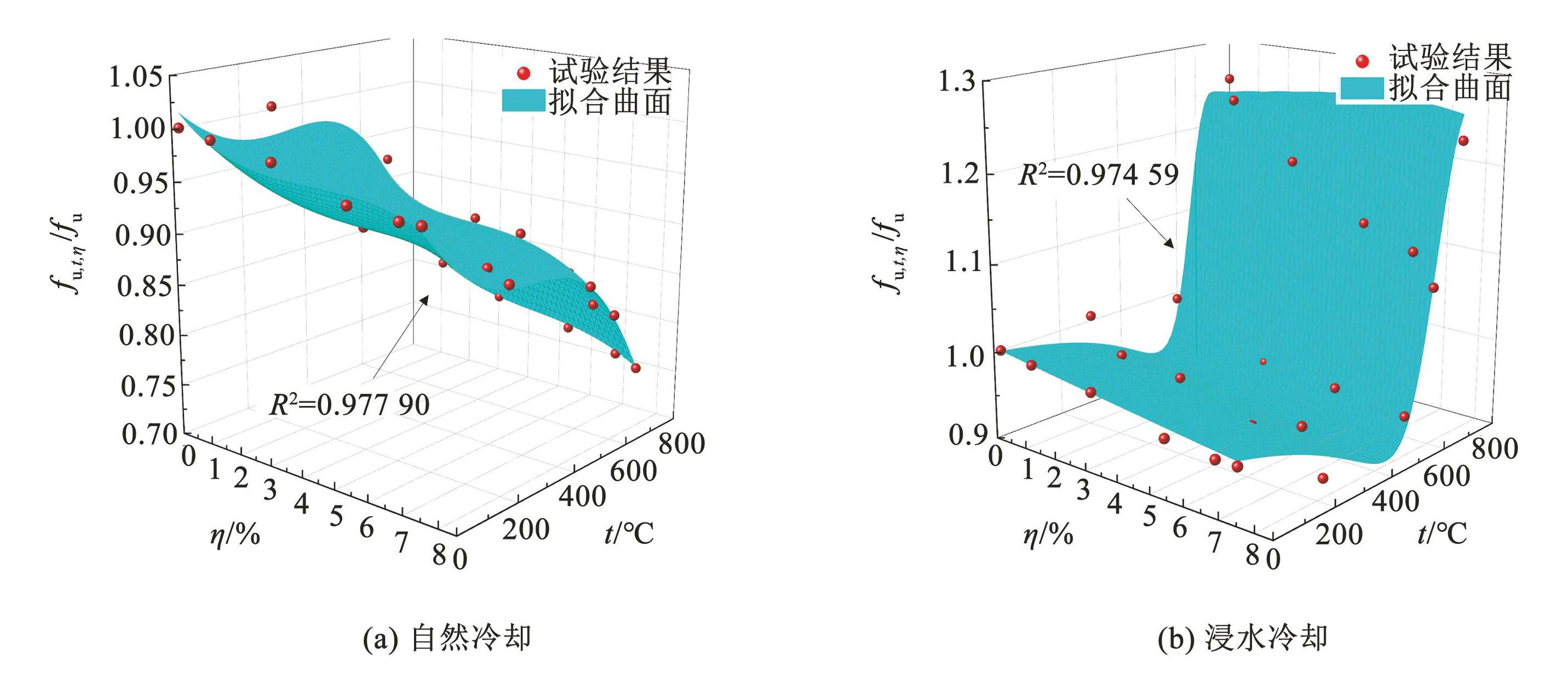
图11极限强度折减系数试验结果与数学模型对比
Fig.11Comparison of test results and mathematical model of ultimate strength reduction factors
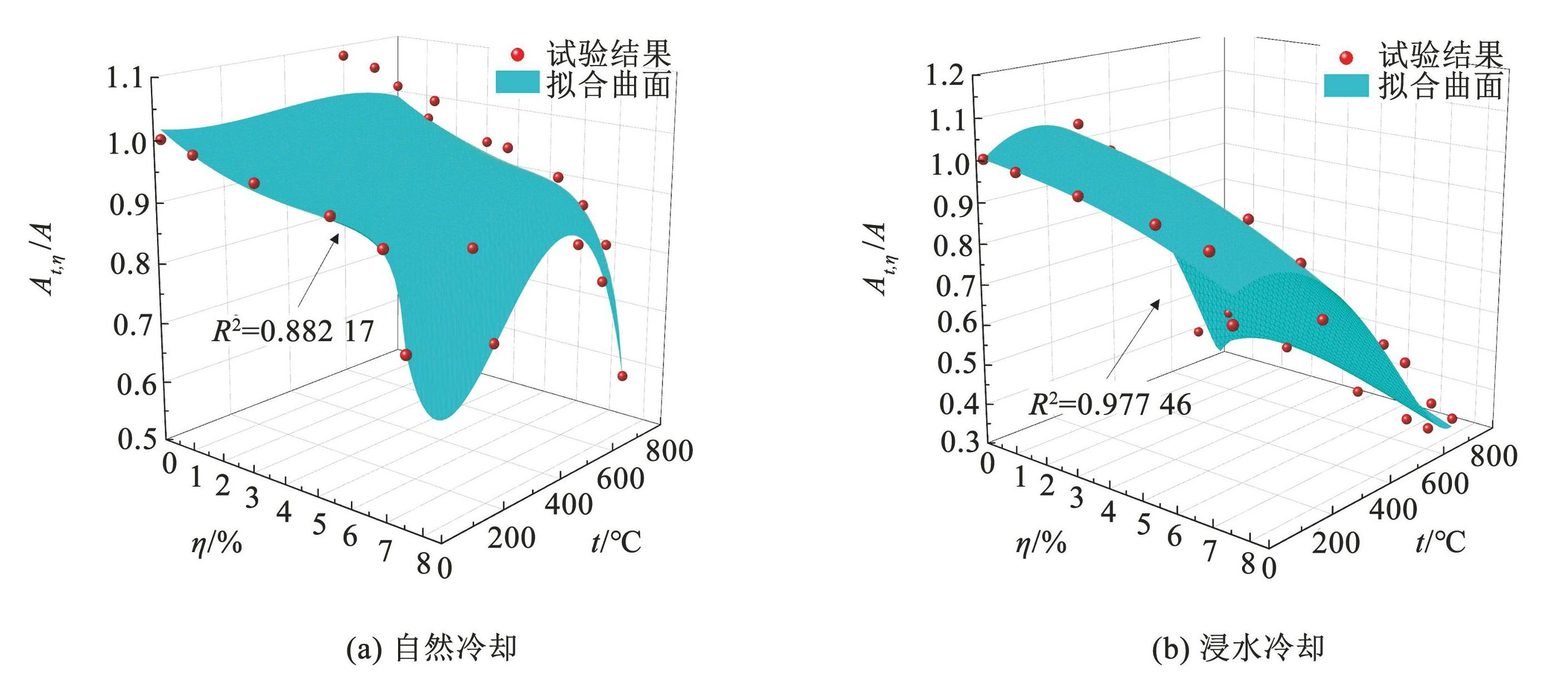
图12伸长率折减系数试验结果与数学模型对比
Fig.12Comparison of test results and mathematical model of elongation reduction factors
3.1 屈服强度
自然冷却方式下:
(2)
浸水冷却方式下:
(3)
3.2 极限强度
自然冷却方式下:
(4)
浸水冷却方式下:
(5)
3.3 弹性模量
弹性模量折减系数表达式为
(6)
3.4 伸长率
自然冷却方式下:
(7)
浸水冷却方式下:
(8)
由图10~12可知,大部分试验数据在拟合曲面上或在拟合曲面周围上下小幅波动,拟合公式(2)~(8)的相关系数 R2均大于 0.88,拟合效果良好。表明式(2)~(8)能较好地反映 S280GD + Z 钢材在锈蚀和高温耦合作用下力学性能变化趋势。
4 本构模型
4.1 本构模型的建立
钢材在单调加载下的应力-应变本构模型主要包括弹性阶段、屈服阶段、塑性强化阶段和颈缩断裂阶段。采用 Esmaeily 和 Xiao [15] 提出的简化二次塑流模型描述 S280GD + Z 钢材骨架曲线,如图13所示。与传统两折线或三折线模型相比,该模型能更好地反映钢材屈服后强化效应。钢材应力-应变关系计算公式如下:
(9)
式中:Es表示钢材弹性模量,f y为钢材屈服强度,εy为钢材本构模型弹性段结束时对应的应变,f u为钢材极限强度。参数 k1和 ku用于控制钢材骨架曲线形状,分别由式(10)和式(11)确定:
(10)
(11)
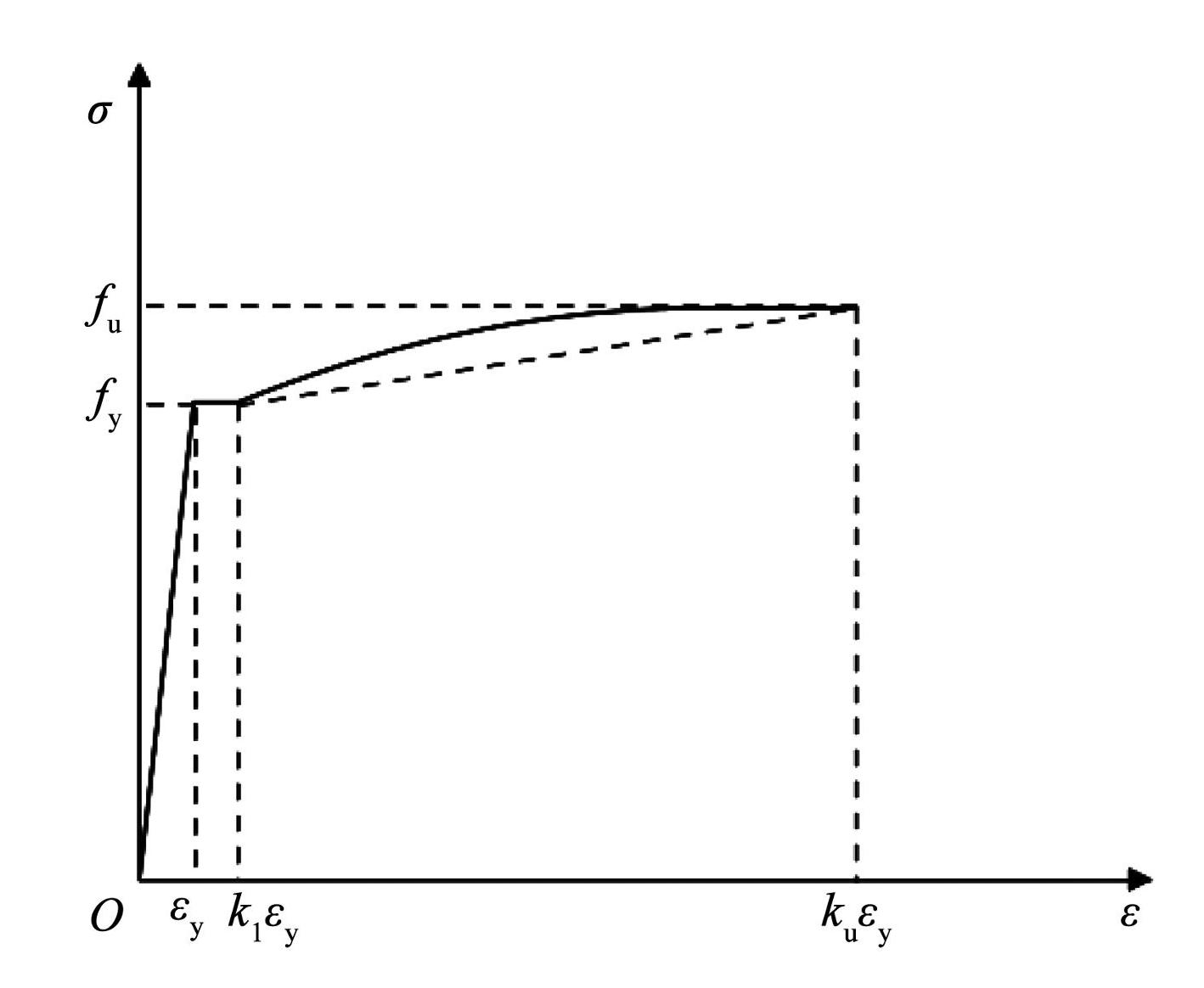
图13简化的二次塑流模型
Fig.13Simplified secondary plastic flow model
4.2 本构模型参数拟合
根据试验结果列出了相关参数,如表3所示。
表3不同冷却方式下骨架曲线参数 ε
Tab.3 Skeleton curve parameters of ε under different cooling methods
表3(续)

采用最小二乘法对 εy进行多项式拟合,拟合结果如图14和图15所示,拟合公式如下。
自然冷却条件下:
(12)
浸水冷却条件下:
(13)
在式(12)和(13)基础上得到 εy拟合值,从而确定骨架参数 k1 、ku,如表4所示。
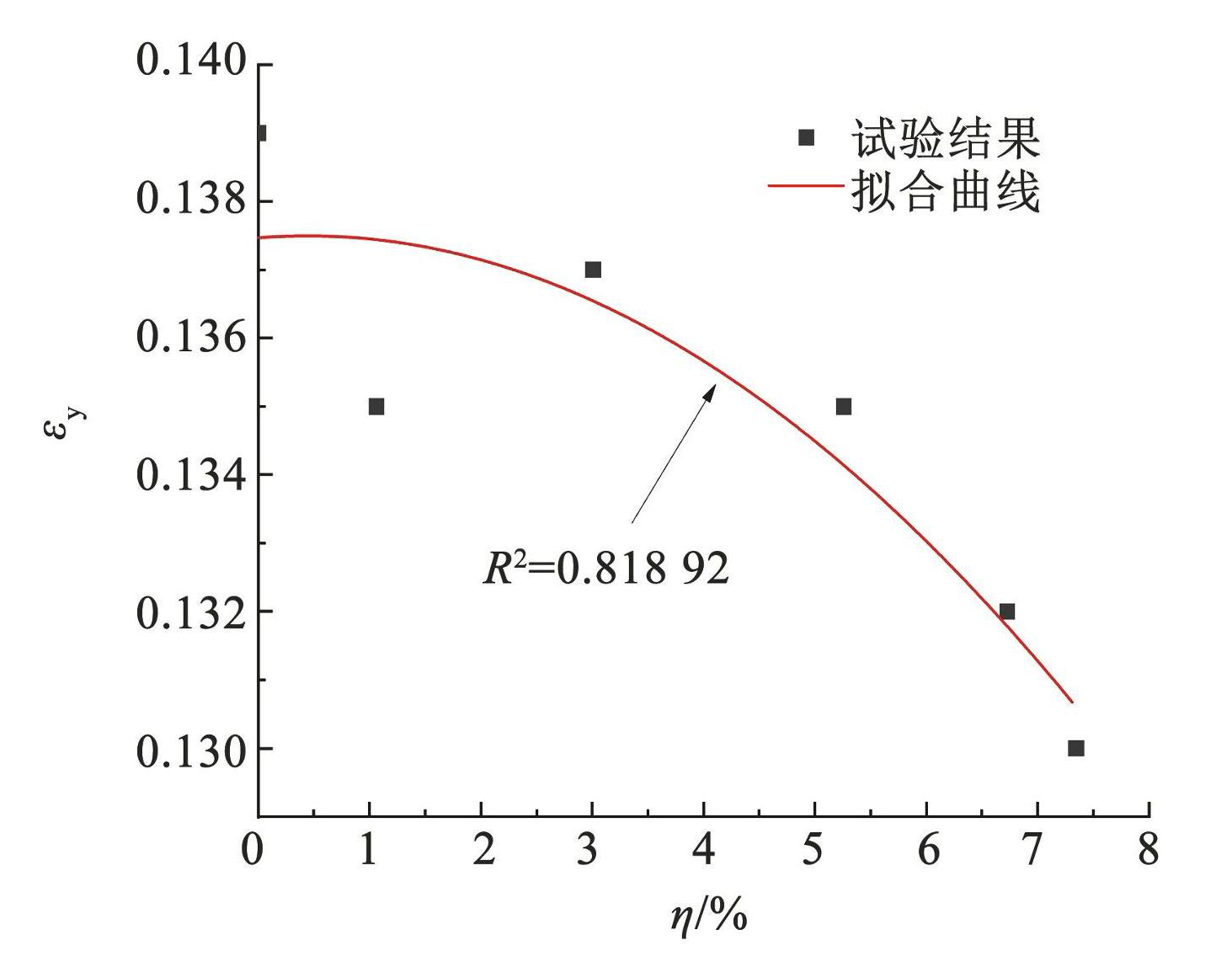
图14自然冷却条件下 εy拟合图
Fig.14Fitting diagram of εy under natural cooling conditions
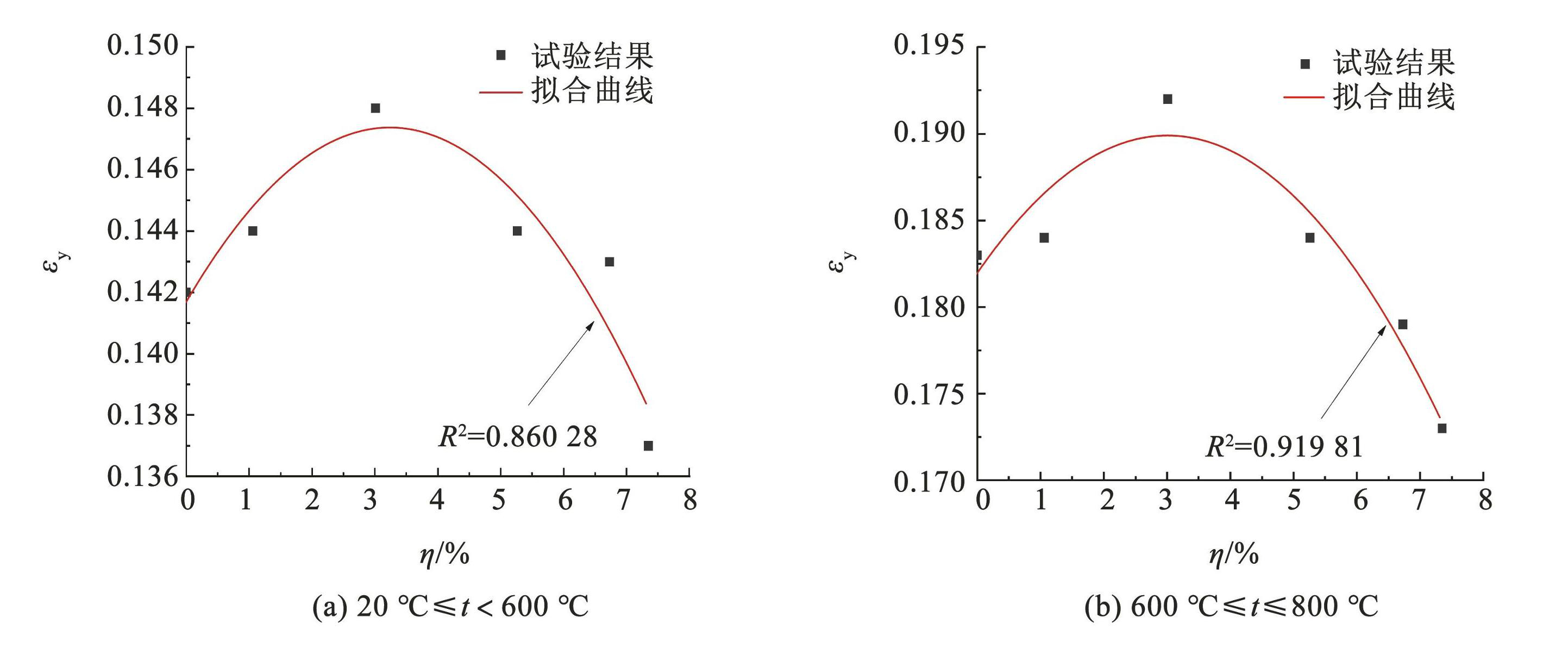
图15浸水冷却条件下 εy拟合图
Fig.15Fitting diagram of εy under water cooling conditions
表4不同冷却方式下骨架曲线参数 k
Tab.4 Parameter k of skeleton curve under different cooling methods

运用 Levenberg-Marquardt 算法对骨架参数 k1、 ku进行二元非线性拟合分析,得到不同冷却方式下 k1和 ku拟合公式,拟合结果如图16和图17所示,拟合公式如下。
自然冷却条件下:
(14)
(15)

图16自然冷却下 k1和 ku拟合图
Fig.16Fitting diagrams of k1 and ku under natural cooling
浸水冷却条件下:
(16)
(17)

图17浸水冷却下 k1和 ku拟合图
Fig.17Fitting diagrams of k1 and ku under water cooling
拟合公式(12)~(17)的相关系数均大于 0.8,可认为该模型参数拟合良好。采用上述拟合公式计算了不同冷却方式下锈蚀 S280GD + Z 钢材高温后单轴受拉应力-应变曲线,受限于篇幅,给出的部分拟合曲线与试验曲线对比如图18所示。可以看出,拟合曲线和试验曲线较为接近,尽管塑性强化阶段曲线与试验曲线有一定误差,但也在允许范围之内,表明所建立模型可以较好地描述在锈蚀与高温耦合作用下 S280GD + Z 钢材单轴受拉本构模型,同时可以预测 S280GD + Z 钢材在高温和锈蚀耦合作用下的单轴受拉本构关系。
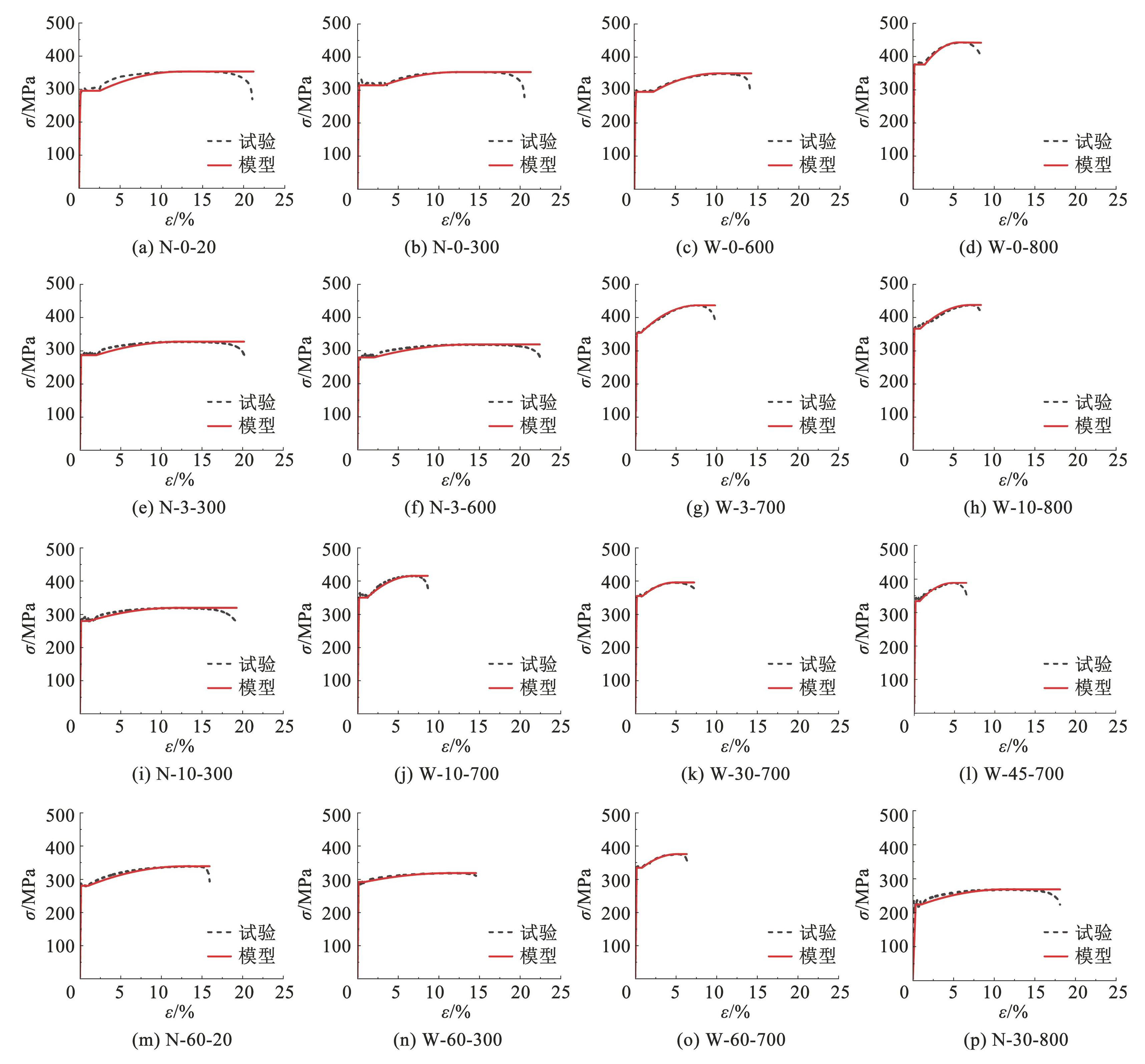
图18所建立本构模型与试验结果对比
Fig.18Comparison between constitutive model and experimental results
5 结论
1)随着锈蚀龄期和受火温度提高,试件表面颜色逐渐变深; 锈蚀龄期大于 45 d 后,不同受火温度试件表面颜色相差不大,均比未锈蚀试件颜色深; 受火温度高于 600℃时,试件开始出现表皮剥离脱落现象,浸水冷却试件剥落更为严重,受火温度高于 700℃ 时,试件表面铁锈完全脱落,试件明显变薄; 自然冷却下试件断口表现出紧缩现象,而浸水冷却试件多为斜向平整断口。
2)不同锈蚀龄期和受火温度下 S280GD + Z 钢材单轴受拉应力-应变曲线形状类似。常温及高温自然冷却下,随着锈蚀龄期增加,钢材极限拉应变变化不明显; 浸水冷却条件下,受火温度低于 600℃ 时,钢材极限拉应变受受火温度影响较小,受火温度高于 600℃时,随着受火温度提高,钢材极限拉应变显著降低,钢材塑性变差。
3)冷却方式、锈蚀程度、受火温度对 S280GD + Z 钢材弹性模量影响较小,对屈服强度、极限强度和伸长率影响较大。锈蚀龄期小于 45 d 时,锈蚀对钢材力学性能影响较小; 受火温度小于 600℃时,受火温度及冷却方式对钢材屈服强度、极限强度影响不显著,但在高温和锈蚀的耦合作用下,钢材力学性能退化幅度增大; 受火温度大于 600℃后,高温在对钢材强度影响中占主导地位。锈蚀龄期超过 45 d 后,锈蚀程度对钢材伸长率影响较大,钢材伸长率会显著较低; 浸水冷却方式下,锈蚀程度对钢材伸长率的影响会随受火温度升高而减弱。
4)建立了锈蚀与高温耦合作用下,屈服强度、抗拉强度和伸长率相对值与锈蚀率和温度之间的定量关系。基于简化二次塑流模型,建立了曲线骨架参数的预测模型,模型曲线与试验曲线吻合良好。
