摘要
结构模型经过有限元方法空间离散化处理之后,可能引入虚假的高频分量,这部分高频分量会对结构的动力响应求解带来不利影响。为此,需要引入算法的数值阻尼有效地抑制这部分虚假的高频分量。使用半显式算法格式,通过匹配隐式 ρ∞ -Bathe 算法放大矩阵的特征方程系数,提出一种具有可控数值阻尼的无条件稳定半显式积分算法,记为 NSE(New Semi-Explicit)- ρ∞ 算法,新算法通过两个自由参数 ρ∞ 和 γ 控制算法的数值阻尼,并且无需对结构运动方程进行加权处理。对新算法的稳定性、精度、周期延长和振幅衰减等数值特性进行分析,结果表明,新算法对于线弹性体系和非线性刚度软化体系均为无条件稳定。通过具有代表性的数值算例,将新算法与两种具有可控数值阻尼的无条件稳定显式积分算法进行对比,证明新算法能够更加有效地抑制虚假高频分量。
Abstract
After the structural model is discretized by the finite element method, it may introduce false highfrequency components that can adversely affect the structural dynamic response of the structure. Therefore, it is necessary to introduce numerical damping into the integration algorithm to effectively suppress these false highfrequency componments. Based on a semi-explicit integration formulation, this paper proposes an unconditionally stable semi-explicit integration algorithm with controllable numerical damping by matching the characteristic equation coefficients of the amplification matrix of the implicit ρ∞ -Bathe algorithm. The new semi-explicit (NSE)- ρ∞ algorithm controls the numerical damping of the integration algorithm by two free coefficients ρ∞ and γ, and does not require weighted equation of motion. The numerical characteristics of the new algorithm, such as stability, accuracy, period elongation and amplitude decay, are analyzed. It is found that the new algorithm is unconditionally stable for both linear elastic and nonlinear stiffness softening systems. Through representative numerical examples, the new algorithm is compared with two other unconditionally stable explicit integration algorithms with controllable numerical damping. The analytical results demonstrate that the new algorithm is more effective in suppressing the spurious high-frequency components.
Keywords
目前,在结构动力学响应的数值计算问题上,比较有效的分析方法仍然是时程分析法[1],即需要求解出整个动态过程中结构的位移、速度和加速度。在分析计算过程中,通常采用积分算法[2] 求解离散化的结构运动方程。经典的积分算法如 Newmark 算法具有较好的精度和适当的计算量,被广泛用于求解结构动力学问题。然而,这些经典算法无法满足求解一些复杂结构动力学问题的需求。以实时混合试验[3-5]为例,当数值子结构为自由度数较多的非线性结构时,如果采用常规的无条件稳定算法(如常平均加速度法),由于算法是隐式,在求解非线性问题时需要迭代,极大增加了求解时间; 如果采用常规的显式算法(如中心差分法),由于算法为条件稳定,需要极小的时间步长以满足稳定性,同样严重影响计算效率,无法满足实时混合试验的实时性要求。
为了解决上述问题,文献[6] 最早提出了同时满足无条件稳定和显式的积分算法,称为 Chang 算法,该算法采用了常平均加速度法的速度表达式,但是位移表达式为显式表达式。由于该算法的积分参数是与结构模型固有属性(质量、阻尼和刚度)相关的变量,文献[7]又将无条件稳定显式算法称为“基于模型的积分算法”。其他有代表性的基于模型的积分算法包括文献[8]提出的 CR 算法、文献[9]提出的 TL 算法。与 Chang 算法不同的是,CR 算法和 TL 算法的速度和位移表达式均为显式,文献[7]将 Chang 算法和 CR/ TL 算法分别称为半显式和双显式算法。文献[10]在 CR 算法的基础上,提出了一族 Gui 算法,与 γ = 1 / 2 的 Newmark 算法有相同的数值特性。为进一步提高算法的精度,文献[11-12] 分别提出一种高阶精度双显式和半显式的基于模型的积分算法。
需要注意的是,上述基于模型的积分算法均不具有数值阻尼,算法的数值阻尼与结构的阻尼功能类似,可以减小结构响应。数值阻尼通常与 Ω = ωΔt(ω 和 Δt 分别为圆频率和时间积分步长)正相关,当算法用于高频时,ω 与 Ω 较大,导致数值阻尼较大,进而算法可以抑制或消除虚假高阶/ 高频响应。其抑制效果与数值阻尼的大小直接相关,数值阻尼也会影响低阶响应的精度,所以,与无数值阻尼的算法相比,有数值阻尼的算法优势在于可以抑制或消除虚假高频分量的影响,缺点在于低阶响应的精度相对较低。因此,设计有数值阻尼算法时,希望低频具有尽量小的数值阻尼,而高频具有尽量大的数值阻尼,即可控的数值阻尼。文献[13] 采用 CR 算法的表达式,通过匹配广义 α(G-α)算法[14] 的数值特性,提出一族具有可控数值阻尼的 KR-α 双显式算法。类似地,文献[15]提出了一族具有可控数值阻尼的 Chang-α 半显式算法。 KR-α 算法和 Chang-α 算法均是引入了额外的加权结构运动方程,应用起来相对复杂,并且数值阻尼仅为单参数控制,不够灵活。文献[16]提出一种与 Newmark 算法数值特性匹配的 GCR 双显式算法,与 Newmark 算法一样,GCR 算法在 γ >1 / 2 且 β≥(γ + 0.5)2 / 4 具有数值阻尼,不过此时算法精度降为 1 阶。文献[17] 在 TL 算法的基础上,提出一种具有可控数值阻尼的 TL-φ 算法,该算法同样存在精度较低的问题。此外,该算法对于无阻尼结构体系并不具有数值阻尼。文献[18]基于隐式 Bathe 算法[19],提出一种具有数值阻尼的无条件稳定显式算法,但是该算法的数值阻尼不可控。
综上,本文采用半显式 Chang 算法的表达式,基于具有可控数值阻尼的隐式 ρ∞-Bathe 算法[20],利用极点配置理论,提出一种具有可控数值阻尼的无条件稳定半显式的 NSE-ρ∞ 算法,与 KR-α 算法和 Chang-α 算法相比,新算法无需引入额外的加权结构运动方程,使用更加方便,具有更加灵活且优异的可控数值特性。
1 新算法的建立
1.1 ρ∞-Bathe 算法
隐式 ρ∞-Bathe 算法具有二阶精度,无条件稳定,且具有可控数值阻尼。需使用两个子步计算 t + Δt 时刻的未知位移、速度和加速度。
在第 1 个子步中,使用梯形规则计算 t + γΔt 时刻的结构响应,格式如下:
(1)
(2)
(3)
在第 2 个子步中,使用 3 点后向欧拉公式计算 t + Δt时刻的结构响应,格式如下:
(4)
(5)
(6)
式中:m,c,k 分别为质量、阻尼系数和刚度; c = 2mξω,ξ 为阻尼比,ω 为圆频率; ,,x 分别为加速度、速度和位移; f 为外界激励; q0,q1,q2,s0,s1,s2 和 γ 为控制算法性能的待定参数。为了使 ρ∞-Bathe 算法具有二阶精度,这些待定参数需要满足下列关系:
(7)
为了在二阶精度的基础上满足无条件稳定的特性,待定参数还需要满足下列关系:
(8)
为了直接规定高频范围内的数值阻尼,建立了 q1 与高频谱半径 ρ∞ 之间的关系:
(9)
至此,ρ∞ -Bathe 算法实际上是关于两个自由参数 γ 和 ρ∞的两子步无条件稳定隐式算法。此外,γ 通常选用范围是(0,2),且应避免取 1 和 2 /(1-ρ∞)。
1.2 新算法积分参数推导(SDOF 体系)
新算法(NSE-ρ∞ 算法)采用 Chang 算法的表达式,对于单自由度( SDOF)体系,其速度、位移差分方程分别如下:
(10)
(11)
将式(4)、(10)和(11)写成递推矩阵的形式:
(12)
式中 为放大矩阵,表达式如下:
(13)
对于 3 × 3 的矩阵,其特征方程可以表示为
(14)
式中:λ 为放大矩阵 的特征值,根据 | -λI | = 0 可以求得 NSE-ρ∞ 算法的特征方程系数为
(15)
令 NSE-ρ∞ 算法与 ρ∞-Bathe 算法的特征方程系数完全相等,即
(16)
通过上式可以求解得到 NSE-ρ∞ 算法在 SDOF 体系下的积分参数。具体表达形式如下:
(17)
(18)
式中常系数 ci ( i = 1~16)取值如下:c1 =(2q1γ-1) 2 γ 2,c2 = 4γ [(2q1γ-1)γ-1](2q1γ-1),c3 =-16(2q1γ-1)γ,c4 =(16 + 4)γ 2-16q1γ + 4,c5 = 16-16(2q1-1)γ,c6 = 16,c7 = 4(2q1-1) 2 γ 2,c8 =-16( 2q1-1)γ,c9 = 4( 2q1-1) 2 γ 2 ,c10 = 16-16(2q1-1)γ,c11 = 16,c12 =-8 ( γ-1) 2 γ2,c13 =-16(2q1-1)q1(γ-1)γ,c14 = 2(2q1-1)(4q1γ-2q1-1)γ 2,c15 = 64q1γ(γ-1)ξ 2 + 8q1γ(-6γ + 4)+ 8γ,c16 = 8。
1.3 新算法积分参数推导(MDOF 体系)
对于线弹性多自由度(MDOF)体系,NSE-ρ∞ 算法的速度、位移差分方程和运动方程如下:
(19)
(20)
(21)
令 Y 为模态坐标系的位移向量,与 X 的关系为 为模态矩阵; ( i = 1,…,n)为第 i 阶振型向量,利用振型的正交性,则式(19)~(21)可以改写至模态坐标系中:
(22)
(23)
(24)
式中为对角型积分参数矩阵。假定阻尼矩阵符合经典阻尼假设,分别为模态质量、阻尼和刚度矩阵。
第 i 阶模态的积分参数可以由 SDOF 体系的积分参数(式(25)、(26))表示,具体如下:
(25)
(26)
式中:分别为第 i 阶模态的质量、刚度和阻尼矩阵,ωi 和 ξi 分别为第 i阶模态的圆频率和阻尼比。从而,模态坐标系下的积分参数矩阵 表达式如下:
(27)
(28)
式中。
最后将 左乘 ,右乘 -1得到 NSEρ∞ 算法用于 MDOF 体系的积分参数矩阵:
(29)
(30)
2 数值特性分析
2.1 稳定性分析
对于线弹性体系,如果放大矩阵的谱半径 ,则积分算法是稳定的。图1为无阻尼 SDOF 体系时 NSE-ρ∞ 算法的谱半径,可知无论参数 ρ∞ 和 γ 取何值,NSE-ρ∞ 算法的谱半径 ρ≤1,即算法在线弹性体系中始终无条件稳定。
接着探究 NSE-ρ∞ 算法在非线性情况下的数值稳定性。利用根轨迹法对算法用于非线性 SDOF 体系的稳定性进行评估。当切线刚度 kt 从 0 增加到 + ∞ 时,根轨迹可以反映不同结构状态的稳定性,包括线弹性、非线性刚度软化和非线性刚度硬化。在 m = 1,ω = 2π,ξ = 0. 02 和 Δt = 0. 02 的条件下,γ 取 0. 05 时,得到 NSE-ρ∞ 算法用于非线性 SDOF 体系的根轨迹图,如图2所示。可以看出,根轨迹均从开环的极点开始,到开环的零点或者无穷远处结束。根轨迹与单位圆交点z =-1 为算法的稳定极限。
式(31)中为 NSE-ρ∞ 算法用于非线性 SDOF 体系的离散闭环传递函数,令其分母的表达式为 0,则为特征方程。将 z =-1 代入式(31)的特征方程中,可以得到 kt / k 的稳定极限,如式(32)所示。
(31)

图1无阻尼 SDOF 体系时 NSE-ρ∞ 算法的谱半径
Fig.1Spectral radius of NSE-ρ∞ algorithm applied to undamped SDOF system
(32)
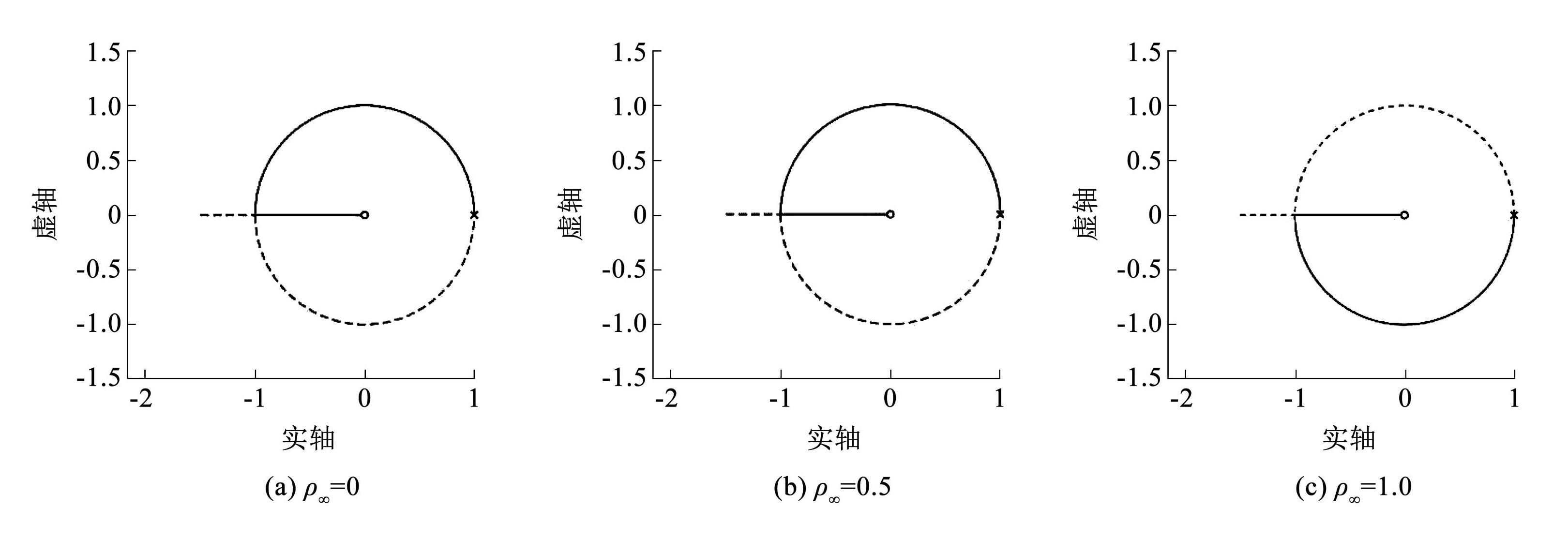
图2NSE-ρ∞ 算法用于非线性 SDOF 体系时的根轨迹(γ = 0. 05)
Fig.2Root loci of NSE-ρ∞ algorithm applied to nonlinear SDOF system (γ = 0. 05)
在 γ 分别取 0. 05、1.99 且 ξ = 0 时求得 NSE-ρ∞ 算法的稳定极限,如图3所示,由图3(a)可以看出,当 γ = 0. 05∈(0,1)且 ρ∞ = 1 时,NSE-ρ∞ 的稳定极限与(kt / k)lim = 1 相切,即 NSE-ρ∞ 算法存在一个不稳定点为 Ω≈9.176,但是其余 ρ∞ 取值的 NSE-ρ∞ 算法对于非线性刚度软化体系和线弹性体系均为无条件稳定。由图3(b)可以看出,当 γ∉(0,1)时,无论 ρ∞ 取何值,NSE-ρ∞ 算法的稳定极限与(kt / k)lim = 1均不存在相切或者相交点,因此,ρ∞ 取任何值时,NSE-ρ∞ 算法对于非线性刚度软化体系和线弹性体系均为无条件稳定。此外,对于非线性刚度硬化体系,相比 KR-α 和 Chang-α 算法,NSE-ρ∞ 算法具有更大的无条件稳定区间,即
(33)
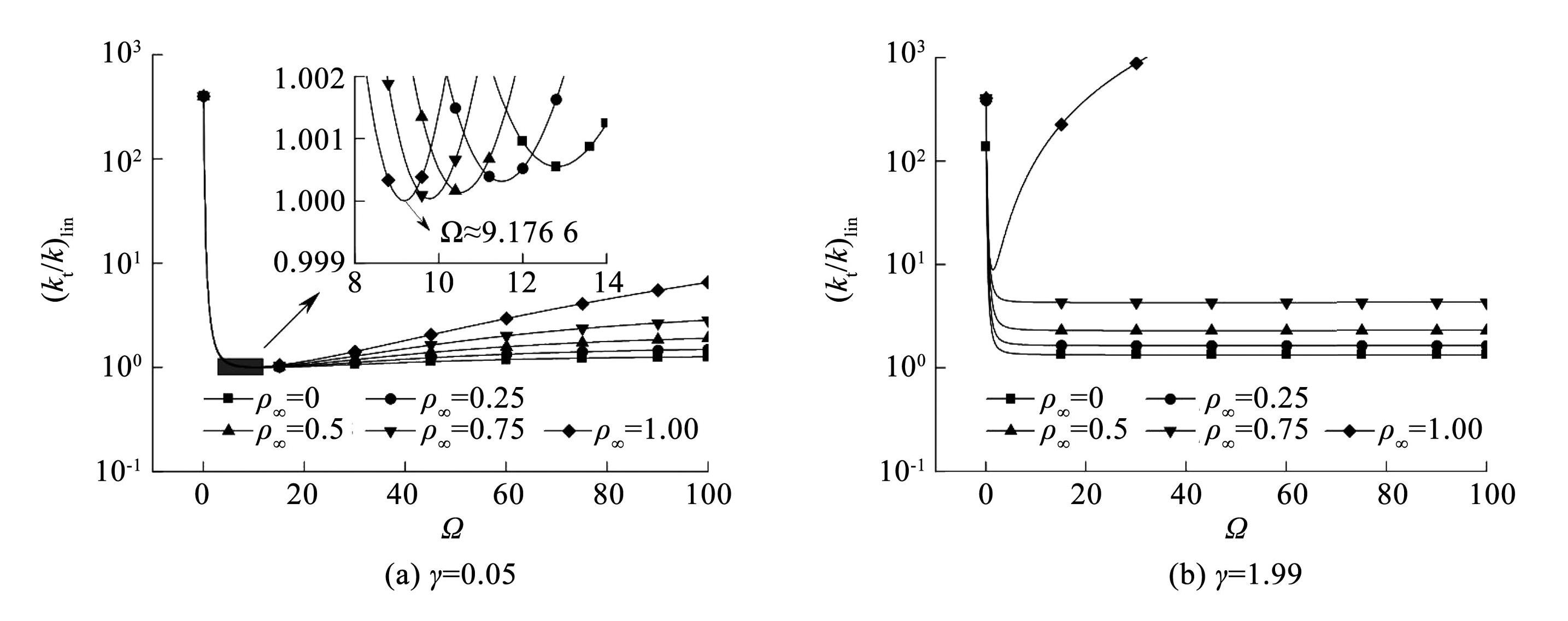
图3NSE-ρ∞ 算法的稳定性极限
Fig.3Stability limits of NSE-ρ∞ algorithm
2.2 精度分析
为了验证 NSE-ρ∞ 算法的数值精度,分析有阻尼线弹性 SDOF 体系在受迫振动时的收敛速率。圆频率 ω = 2π,初位移和初速度均为 1,计算持续时间 t = 1 s,阻尼比 ξ = 0. 05,外界荷载 f(t)= sin(πt)。
图4为当 γ = 1.5 时,NSE-ρ∞ 算法的收敛速率。可以看出,新算法对于位移、速度和加速度均能保持二阶数值精度,ρ∞ 的取值影响计算误差的大小,基本的趋势为 ρ∞ 越大,计算误差越小。
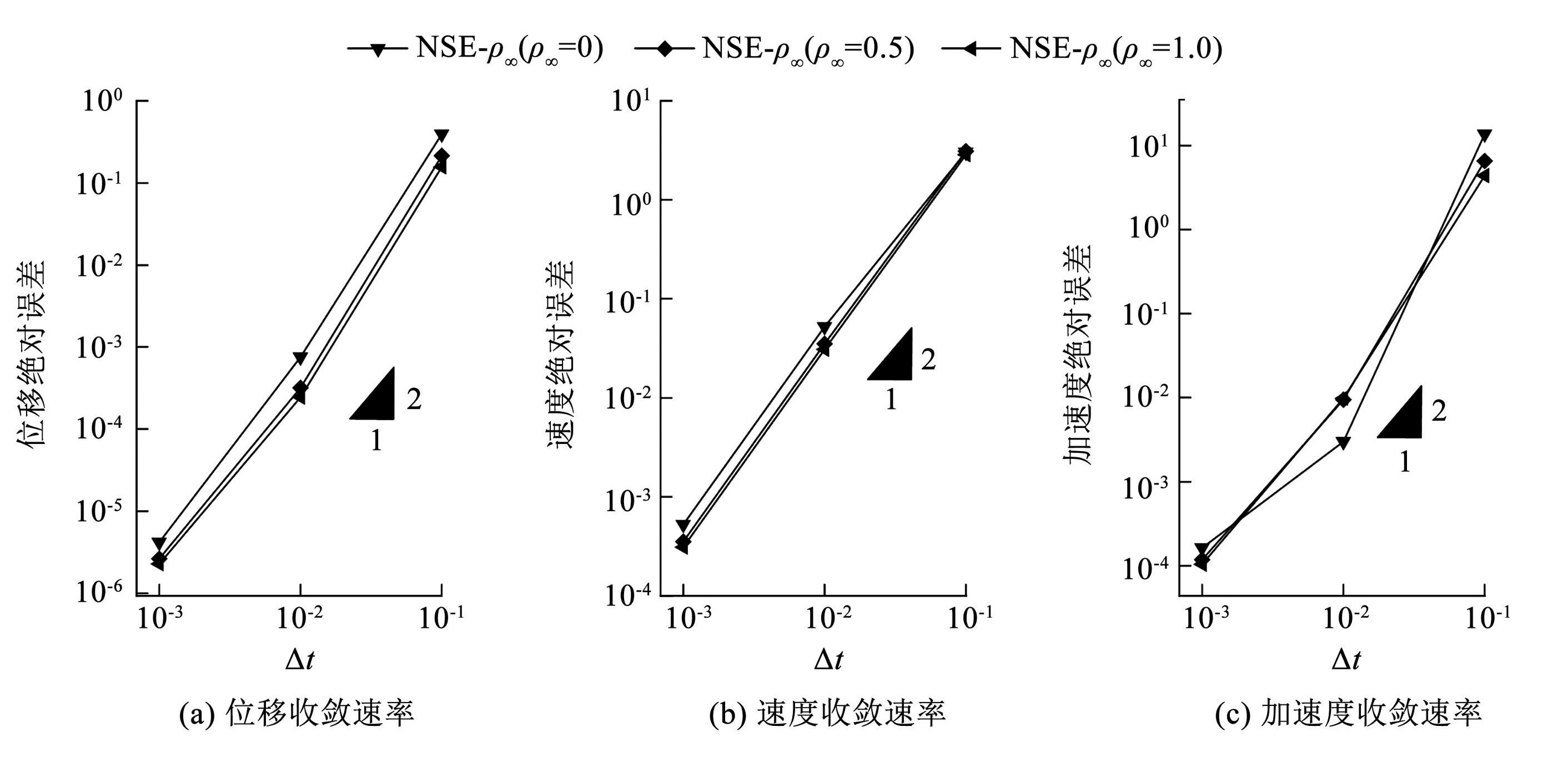
图4NSE-ρ∞ 算法的收敛速率(γ = 1.5)
Fig.4Convergence rates of NSE-ρ∞ algorithm (γ = 1.5)
2.3 周期延长和振幅衰减
除收敛速率外,周期延长(period elongation,EP)和振幅衰减( amplitude decay,DA )是两项可以衡量积分算法准确性的指标。具体计算公式如下:
(34)
(35)
式中: ,T0 为无阻尼 SDOF 结构体系的自振周期。数值阻尼比 和表观频率 的表达式如下:
(36)
(37)
式中:σ 和 ε 分别为算法放大矩阵 A 特征值的实部与虚部。
由于算法涉及到两个自由参数 γ 和 ρ∞,采用控制变量的方法分别对 γ 和 ρ∞ 对 EP和 DA的影响进行分析。
图5给出了当 ρ∞ = 0.5 且 γ∈(1,2)时,NSEρ∞ 算法的 EP和 DA。可以看出,当 ρ∞ 取定值时,EP 和 DA随着 γ 的增大均一直增大。
图6为当 γ = 1.5 且 ρ∞ ∈[0,1]时,NSE-ρ∞ 算法的 EP和 DA。可以看出,当 γ 取定值时,EP和 DA随着 ρ∞ 的增大均一直减小。

图5NSE-ρ∞ 算法的周期延长和振幅衰减(ρ∞ = 0.5,γ∈(1,2))
Fig.5Period elongation (EP) and amplitude decay (DA) of NSE-ρ∞ algorithm (ρ∞ = 0.5, γ∈ (1, 2) )
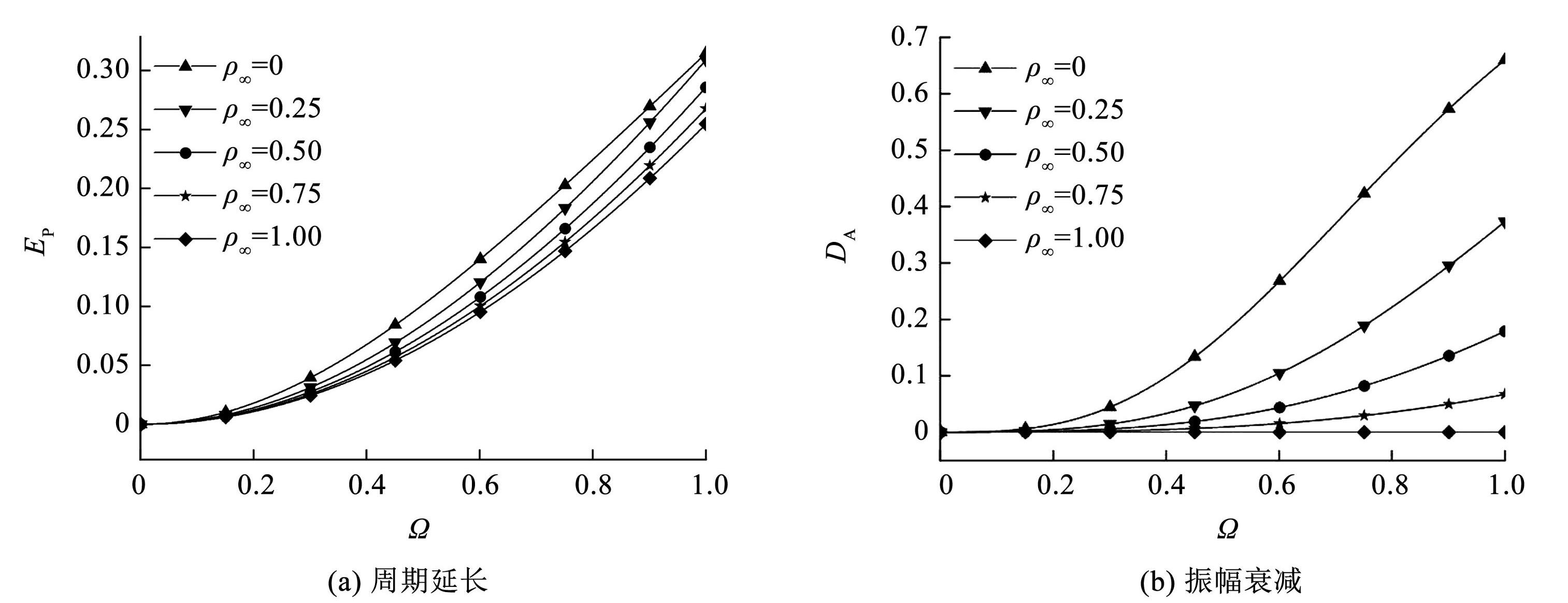
图6NSE-ρ∞ 算法的周期延长和振幅衰减(γ = 1.5,ρ∞ ∈[0,1])
Fig.6Period elongation (EP ) and amplitude decay (DA ) of NSE-ρ∞ algorithm (γ = 1.5, ρ∞ ∈[0, 1])
通过上述分析可以得到,NSE-ρ∞ 算法在 γ = 1.99(非常接近 γ 选值范围的上限)且 ρ∞ = 0 时,抑制虚假高频分量的能力非常强,将在下一节通过数值算例进一步验证。
图7对比了 NSE-ρ∞ 算法与 GCR、KR-α、Chang-α、ρ∞ -Bathe 等算法的 EP 和 DA,可以看出: KR-α 和 Chang-α 具有相同的 EP和 DA,因为他们的数值特性均与 G-α 算法匹配; NSE-ρ∞ 和 ρ∞-Bathe 的 EP和 DA 相同; GCR 的 EP最大,而 NSE-ρ∞ 和 ρ∞ -Bathe 的 EP 最小,具有最优的精度。
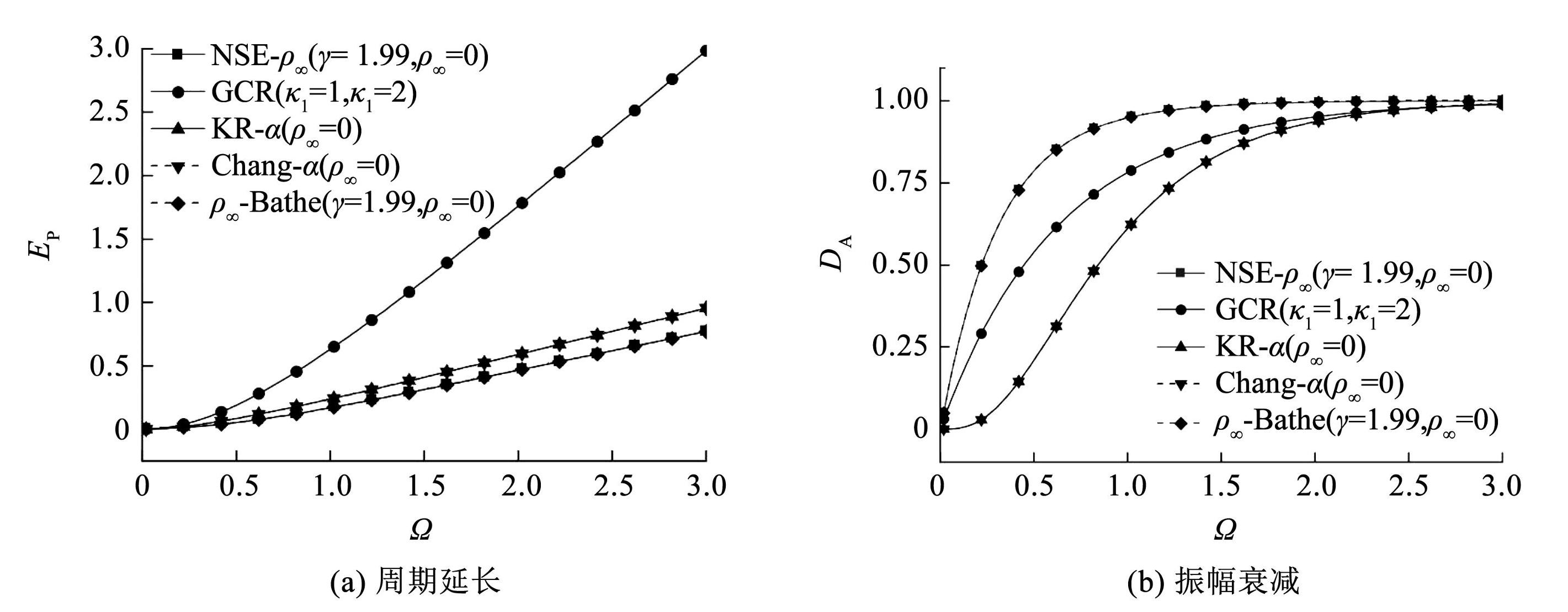
图7几种积分算法的周期延长和振幅衰减对比
Fig.7Comparisons of period elongation (EP ) and amplitude decay (DA ) for different integration algorithms
3 数值算例
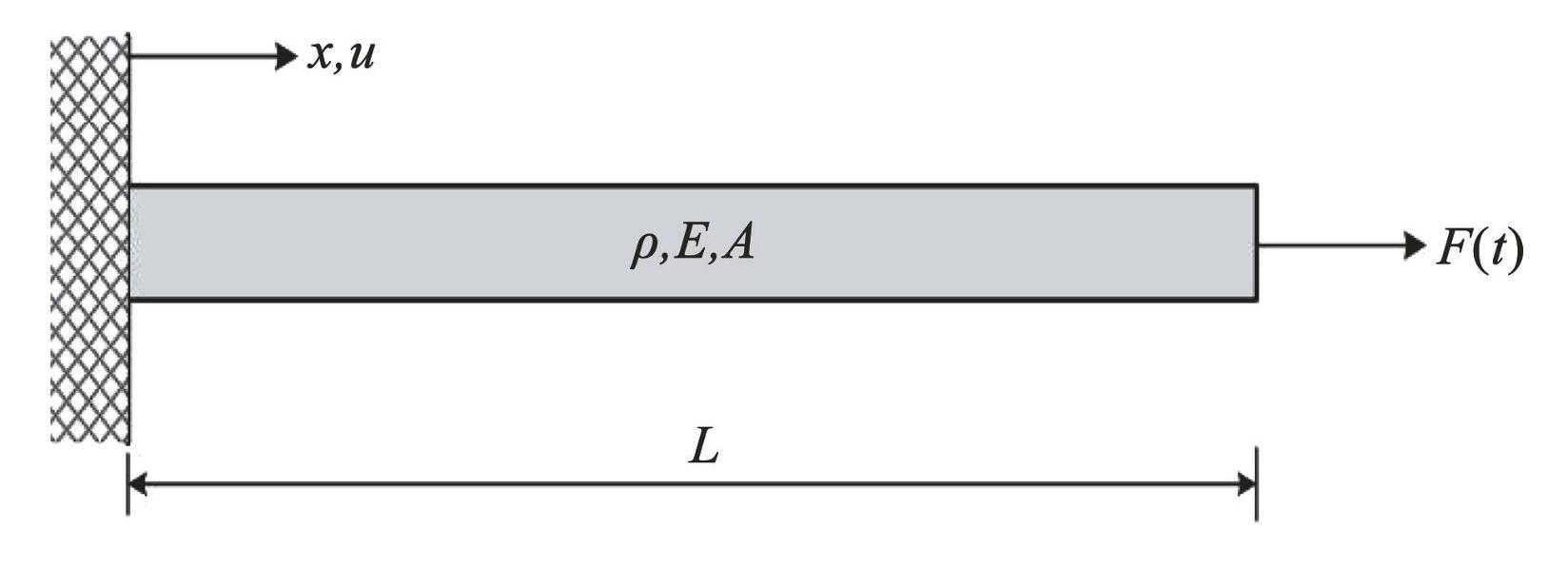
图8轴向荷载激励的自由固支杆件
Fig.8Free-fixed bar subjected to axial load excitation
该模型参数均设置为无量纲数,轴向荷载 F(t)= 10 4,材料的杨氏模量 E = 3 × 10 7,材料密度 ρ = 7.3 × 10-4,横截面面积 A = 1,杆件长度 L = 200。有限元数值模型使用 N = 200 个等长 l = L / N 的两节点线性单元集成。该模型的整体集中质量矩阵 M 和刚度矩阵 K 分别计算如下:
(38)
(39)
计算该固支杆件中心处的位移和速度时程响应,其位移精确解为
(40)
(41)
式中 c 表示波在杆件中的传播速度。
使用时间步长 Δt = 9.88 × 10-7 的 KR-α 算法(ρ∞ =0)、Chang-α 算法(ρ∞ =0)、G-α算法( ρ∞ = 0)、 NSE-ρ∞ 算法(γ = 1.99,ρ∞ = 0)、ρ∞-Bathe 算法(γ = 1.99,ρ∞ = 0)作为数值解,各算法均选择对应的最大数值阻尼参数,以便于进一步比较各算法对虚假的高频分量抑制能力的强弱。此外,选用 NSE-ρ∞ 算法(γ = 1.99,ρ∞ = 1)作为对比,此时,该算法的数值阻尼最小。
图9和图10分别给出了固支杆件中心处的位移和速度时程响应。可以看出,无论对于位移的求解或是速度的求解,当选用最大数值阻尼参数时,KR-α、Chang-α 和 G-α 算法结果接近,而 NSE-ρ∞ 和 ρ∞-Bathe 算法结果接近,相比 KR-α、Chang-α 和 G-α 算法对虚假的高频分量有更强的抑制能力。而对于具有最小数值阻尼的 NSE-ρ∞ 算法(γ = 1.99,ρ∞ = 1),其抑制虚假高频分量的能力明显弱于其他算法,特别是对于速度的求解(图10)。
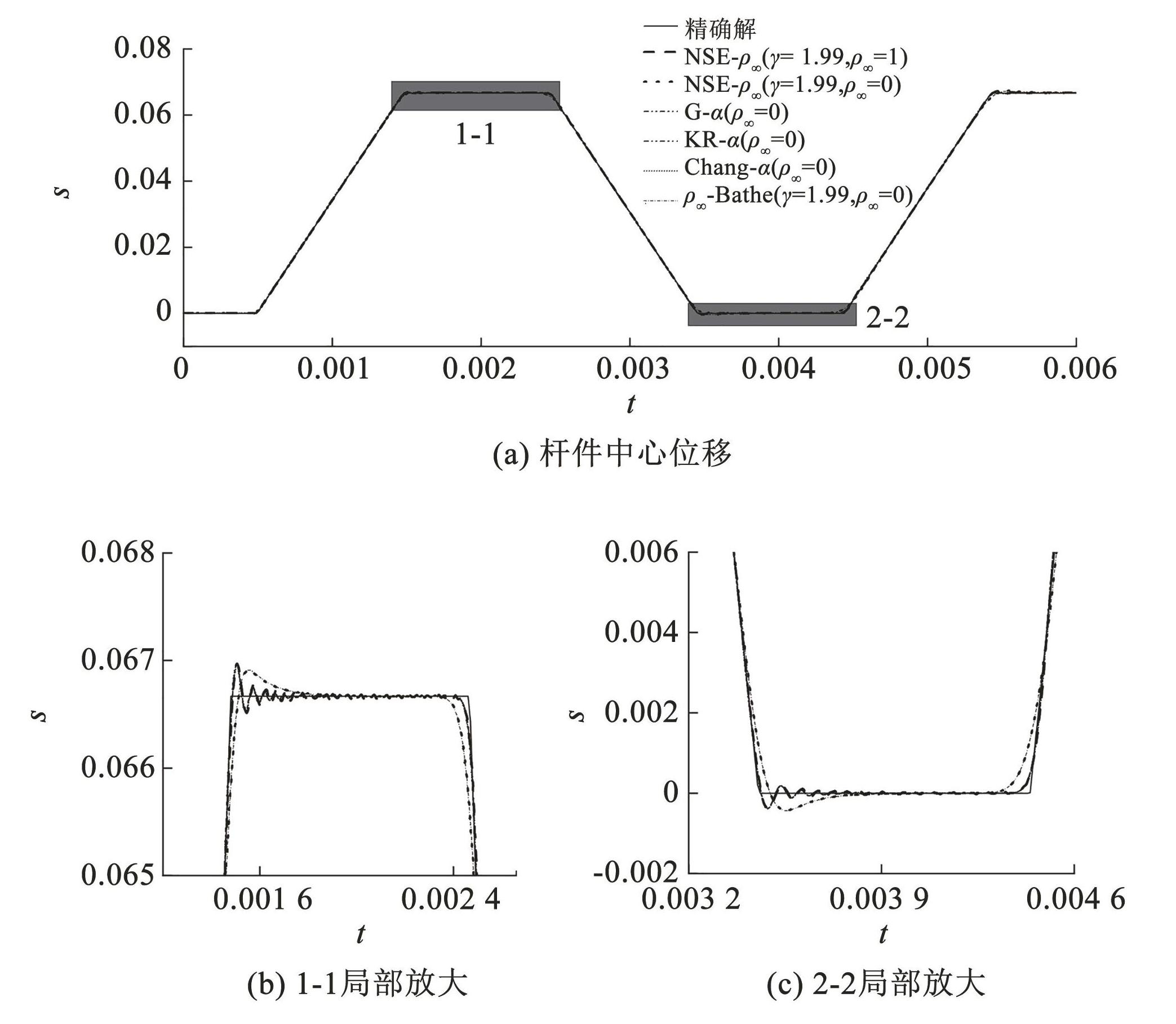
图9杆件中心的位移-时程响应
Fig.9Displacement-time history response of bar center
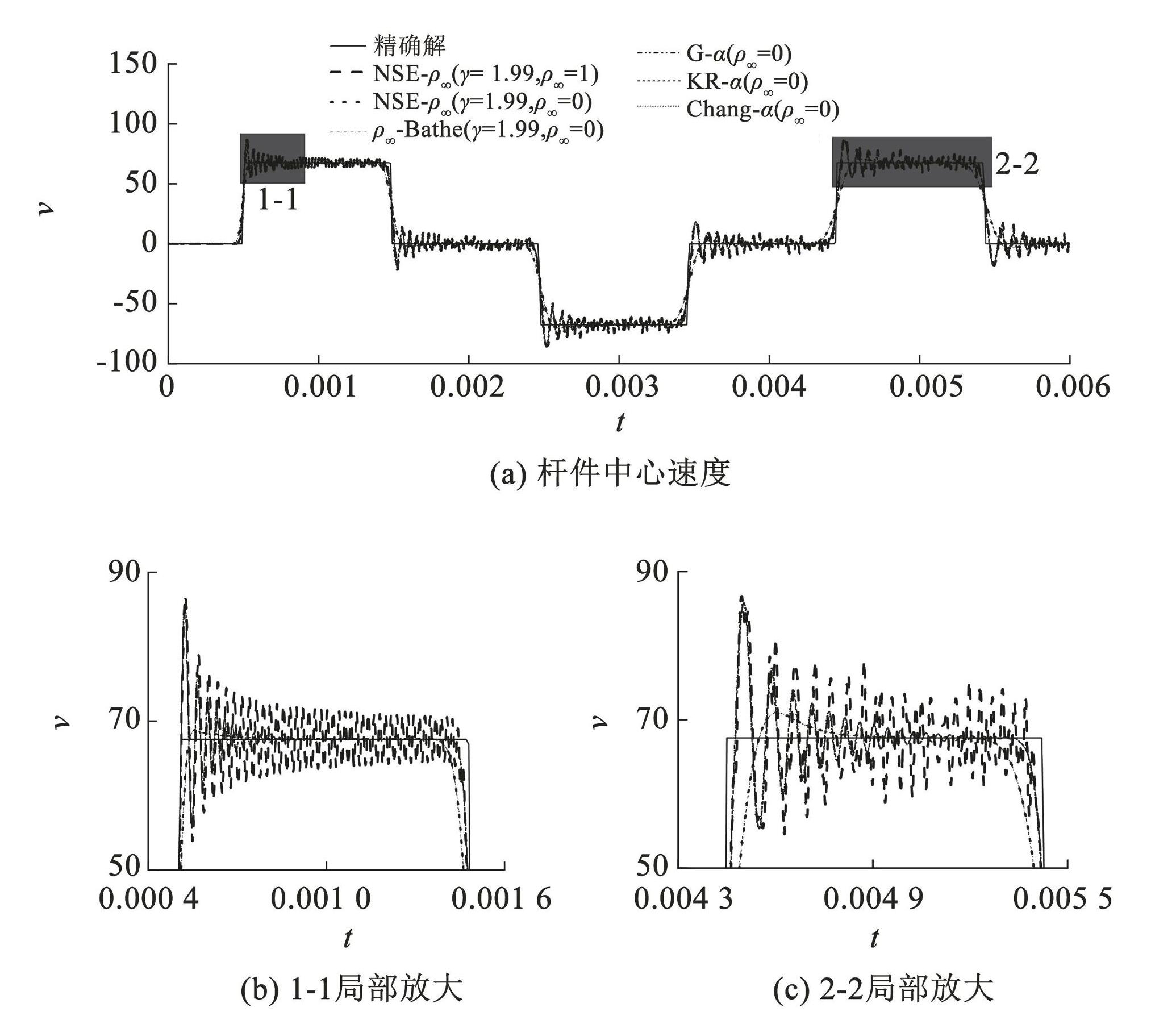
图10杆件中心的速度-时程响应
Fig.10Velocity-time history response of bar center
4 结论
本文采用半显式的算法格式,提出了一种具有可控数值阻尼的基于模型的积分算法,即 NSE-ρ∞ 算法。该算法与两子步无条件稳定的 ρ∞ -Bathe 隐式算法具有相同的特征根。 NSE-ρ∞ 算法不需要引入额外的加权运动方程使算法具有可控的数值阻尼,因此,算法格式更精简。此外,新算法由两个自由参数 γ 和 ρ∞ 控制算法的数值阻尼,相比 KR-α 算法和 Chang-α 算法仅使用一个自由参数 ρ∞ 控制算法的数值阻尼,新算法无疑具有更加灵活的数值阻尼可控性。通过具有代表性的数值算例说明了 NSE-ρ∞ 算法能够更为有效地抑制虚假高频分量。根据研究结果得到如下结论:
1)NSE-ρ∞ 算法兼具显式、无条件稳定和可控数值阻尼的优点。以非常简单的算法格式,给算法引入了更加灵活可控的数值阻尼。
2)NSE-ρ∞ 算法的数值阻尼由两个自由参数 γ 和 ρ∞ 控制,其中,γ 的取值范围为(0,2),但应避免取 1 和 2 /(1-ρ∞); ρ∞ 的取值则更为简单,仅需满足[0,1]即可。
3)NSE-ρ∞ 算法对于线弹性体系和非线性刚度软化体系均为无条件稳定,对于非线性刚度硬化体系,相比 KR-α 和 Chang-α 算法,NSE-ρ∞ 算法具有更大的无条件稳定区间。
4)无论是对于位移的求解还是速度的求解,NSE-ρ∞ 算法对虚假的高频分量具有非常强的抑制能力。
