2. 沈阳建筑大学 机械工程学院,沈阳 110168
2. School of Mechanical Engineering, Shenyang Jianzhu University, Shenyang 110168, China
电主轴单元作为数控机床的主要功能性部件,其振动特性对工件的加工质量有直接影响.由于其特殊的物理构造以及使用变频器驱动,电源中的谐波会使电主轴产生电磁谐波,进而产生电磁振动[1],电主轴的运行特性亦会受到影响.因此,为了减少电磁谐波,进而提高控制性能,就要分析出控制模式下变频器电磁谐波的特性及振动特点[2].
采用直接转矩控制(direct torque control, DTC)作为电主轴的变频控制模式,其核心为PWM调制技术[3],其优点是从CPU及外围控制电路到变频器都是以数字电路实现的.本文尝试在DTC中融入空间矢量脉宽调制(space vector pulse width modulation, SVPWM)的控制方法,并给出了控制系统的设计和实验结果.
1 融入SVPWM的DTC控制技术DTC利用定子的定向磁链,可以对转矩进行直接控制[4].重要的是如何在每个周期里选出合适的电压矢量,并要时刻保证转矩在t=0时可以快速地向着设定的方向变化.电压矢量的选择方法采用预期电压法[5]:“首先,根据转矩偏差、磁链偏差和转速计算出一个能达到最佳控制的预期电压; 然后,用电压型逆变器的6个工作电压中与之相邻的两个电压矢量来合成[6],计算出各自的工作时间; 最后用零电压补足采样周期”.
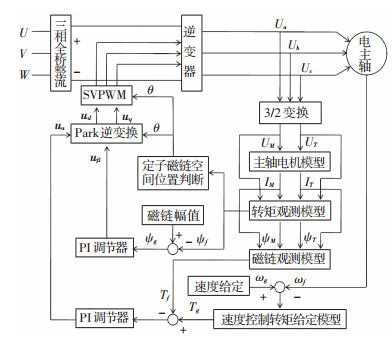
如图 1所示,融入SVPWM后,利用旋转坐标变换[7],把观测到的磁链和转矩转换成αβ坐标系下的电压控制量uα和uβ, 结合定子旋转角度θ,通过Park逆变换转换成dq坐标系下的电压ud和uq,再利用SVPWM转换成实际的三相电压量来完成对电主轴转矩的控制[8].
|
图 1 改善型DTC框图 Figure 1 Block diagram of improved DTC |
磁链及转矩的偏差越细化[9],预期的电压空间矢量的作用越精确,不仅能改善DTC系统的静态和动态性能,也能减小电磁磁链和电磁转矩的脉动[10-11]. 图 2中显示了8个基本电压空间矢量,其中非零向量的幅值相同、模长为2U/3,相邻矢量的间隔60°,两个零矢量的幅值为零,位于中心点.在任意时刻,选择零向量和两个非零的电压空间矢量,都可以根据伏秒平衡的原理去合成任意的电压空间矢量[12],即
| $ {{\boldsymbol{U}}_{\text{out}}}*T={{U}_{x}}*{{T}_{x}}+{{U}_{y}}*{{T}_{y}}+{{U}_{z}}+*{{T}_{z}}. $ | (1) |

|
图 2 圆形磁链轨迹示意 Figure 2 Schematic diagram of circular flux track |
使用电压矢量合成技术,预期的电压向量从U4(100)点开始操作,每次增加或者减少一个微小的量,而变化后的电压矢量可以由相邻的非零基本向量与
把磁链轨迹分为6个区域,每个区域占60°,分别标以Ⅰ,Ⅱ,…,Ⅵ.用|Ψg|表示定子磁链实时幅值[14],用|Ψf|作为两个圆的半径差,Δ|Ψf|表示允许的误差,为了保证定子磁链矢量的幅值仅在设定幅值|Ψg|的允许偏差Δ|Ψf|/2内变化,在不同的时间段内选择适当的电压空间矢量[15],即
| $ \left| {{\boldsymbol{\psi} }_{g}} \right|-\vartriangle \left| {{\boldsymbol{\psi} }_{f}} \right|/2\le \left| {{\boldsymbol{\psi} }_{f}} \right|\le \left| {{\boldsymbol{\psi} }_{g}} \right|+\vartriangle \left| {{\boldsymbol{\psi} }_{f}} \right|/2. $ | (2) |
在电主轴转动时,任何一个时间上电压空间矢量的选择,需要依据磁链偏差程度, 并且要考虑磁链所处的方向[16].当定子磁链|Ψf|位于Ⅱ区域内,并有|Ψg|-Δ|Ψf|/2的值,如果要求定子磁链逆时针方向旋转时,需要依次使用电压矢量U2及U3,这样就可以使|Ψf|满足式(2).为了获取预期的电压矢量调制信号Uout,可以根据矢量图解析获得所需的基本电压空间矢量以及旋转角度θ,进而去驱动功率开关元件动作.实验取18°为增量,推导出时间系数见表 1,乘以Ts/(360/18)可计算出式(1)中Tx、Ty、Tz,在电压矢量转动一周时, 电压周期的正弦波形即可由逆变器中输出.
| 表 1 时间系数 Table 1 Time coefficient |
由以上结果可推出,无论定子的磁链处于任何区域,电压空间矢量U0~U7都可以任意使用.任何一个电压空间矢量都会影响到定子磁链和电磁转矩,根据定子磁链位置检测信号θ、ud和uq来挑选电压矢量进行控制,即可获得圆形的磁链轨迹,并且其电磁转矩脉动量也会变小.
3 硬件电路的搭建采用DSP控制器, 将控制算法烧写到DSP中,用串口指令通过IGBT驱动板对IGBT开关模块精确操作, 以完成对电主轴的控制.放置传感器:1#前端垂直径向、2#前端水平径向、3#前端轴向,连接振动分析仪测试其电磁振动特性. DSP选用TMS320F2812PGFA,IGBT选用FS200R12PT4模块, 驱动电路选用AST965,三相整流桥选用MDS100A1800V模块,选用实验室自行设计、型号为150MD18Z9的两对极对数的电主轴,额定电压380 V,额定频率1 000 Hz,额定转速是30 000 r/min,IGBT的开关频率选择20 kHz(360/18*1 000 Hz),本文实验选择最高转速18 000 r/min,系统有很大的冗余满足该实验.
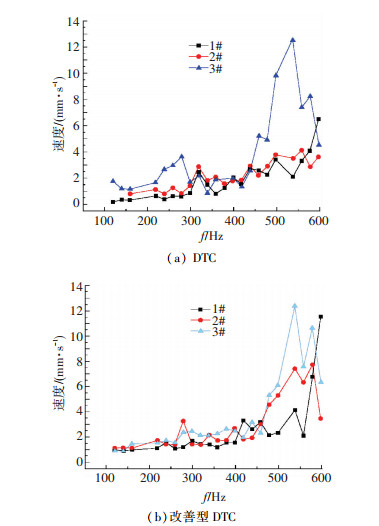
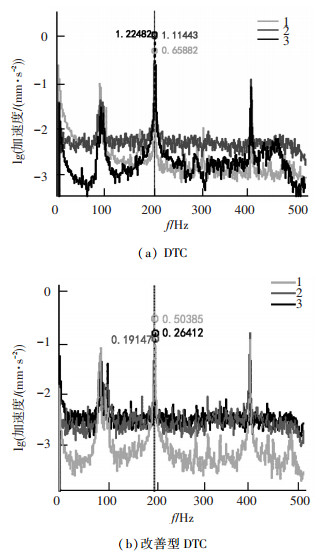
4 实验结果分析在相同实验条件下,传统DTC与改善型DTC的实验结果见图 3,4.由图 3,4可知:
|
图 3 电主轴电磁振动速度 Figure 3 Electromagnetic vibration speed of electric spindle |
|
图 4 电主轴电磁振动加速度频谱 Figure 4 Electromagnetic vibration acceleration frequency spectrum of electric spindle |
1) 实验频率运行在100~450 Hz时,改善型DTC各个方向上振动速度的振动幅值有明显减小,特别是前端轴向的振动速度下降30%左右;
2) 实验频率运行在450~600 Hz时,电主轴的轴向振动速度及水平振动速度均明显增大,且大于其前端垂直径向振动速度;
3) 实验频率在200 Hz时,振动加速度的幅值在垂直径向由0.658 82 m/s2变为0.503 85 m/s2, 水平径向由1.114 3 m/s2变为0.191 47 m/s2, 轴向由1.224 84 m/s2变成0.264 12 m/s2,其水平径向和轴向的振动明显变小.
综上, 可以给出如下结论:在改善型DTC控制下,各方向振动速度在各个运行频率、特别是100~450 Hz时的转矩脉动明显减小,水平径向和轴向的振动加速度的幅值在200 Hz时大幅减小,其动态性能得到明显改善.
5 结论1) 本文在研究DTC控制策略的基础上,融入了SVPWM控制技术,有效地改善电主轴的运行特性,对于高性能的电主轴的控制设计具有一定的指导参考价值;
2) 针对电主轴的振动问题从控制策略角度,提出了控制性能改善的措施,通过对电主轴电磁振动速度及加速度实验,验证了改善型DTC控制策略对降低振动幅值的有效性.
| [1] |
吴玉厚.
数控机床电主轴单元技术[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2006 : 25 -37.
WU Yuhou. Electric spindle unit technology of CNC machine tools[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2006 : 25 -37. |
| [2] |
熊万里, 吕浪, 阳雪兵, 等. 高频变流诱发的电主轴高次谐波振动及其抑制方法[J].
振动工程学报,2008, 21 (6) : 600-607.
XIONG Wanli, LV Lang, YANG Xuebing, et al. High-order harmonic vibration of motorized spindle caused by high-frequency converting current and the suppressing methods[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering,2008, 21 (6) : 600-607. |
| [3] | BOGLIETTI A, FERRARIS P, LAZZARIi M, et al. Influence of the inverter character on the iron losses in PWM inverter-fed induction motors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications,1996, 32 (5) : 1190-1194. DOI: 10.1109/28.536882 |
| [4] | ABDELHALIM T, OUAHID B, KHELIFA B, et al. Direct torque control (DTC)strategy based on fuzzy logic controller for a permanent magnet synchronous machine drive[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering and Technology,2009, 4 (1) : 66-78. DOI: 10.5370/JEET.2009.4.1.066 |
| [5] |
张翊诚, 陈吉红, 唐小琦, 等. 改进型直接转矩控制在高速电主轴上的应用[J].
电机与控制应用,2008, 35 (9) : 26-29.
ZHANG Yicheng, CHEN Jihong, Tang Xiaoqi, et al. Application for enhanced direct torque control of high speed motorized spindle[J]. Electric Machines & Control Application,2008, 35 (9) : 26-29. |
| [6] | BROECK H W, SKUDELNY H C, STANKE G V. Analysis and realization of a pulse width modulator based on voltage space vectors[J]. IEEE Trans, IA,1988, 24 (1) : 142-150. |
| [7] |
巫庆辉, 邵诚, 许占国. 直接转矩控制技术的研究现状与发展趋势[J].
信息与控制,2005, 34 (4) : 444-450.
WU Qinghui, SHAO Cheng, XU Zhanguo. Survey of research status quo and development trends about direct torque control[J]. Information and Control,2005, 34 (4) : 444-450. |
| [8] | SOLTANI J, ARAB MARKADEH G R, HOSSEINNY S H. A new adaptive direct torque control (DTC) scheme based-on SVM for adjustable speed sensorless induction motor drive[C]//The 30th annual conference of the IEEE industrial electronics soelaty. Busan:[s.n.], 2004: 1111-1116. |
| [9] | BOGLIETT A, CAVAGNINO A L M. Fast method for the iron loss prediction in inverter-fed induction motors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications,2010, 46 (2) : 806-811. DOI: 10.1109/TIA.2010.2040055 |
| [10] | WANG H, XU W, SHEN T, et al. Stator flux and torque decoupling control for induction motors with resistances adaptation[J]. IEE Proc Control Theory Appl,2005, 154 (4) : 363-370. |
| [11] | NASH J N. Direct torque control, Induction motor vector control without an encoder[J]. lEEE Transactions on Industry Applications,1997, 33 (3/4) : 333-341. |
| [12] | CASADEI D, GRANDI G. Effects of flux and torque hysteresis band amplitude in direct torque control of induction machines[J]. Industrial Electronics, Control and Instrume-ntation,1994 (1) : 299-304. |
| [13] |
张云, 吴凤江, 孙力, 等. 异步电动机铁耗对直接转矩控制性能的影响及补偿方法[J].
电工技术学报,2008, 23 (9) : 51-56.
ZHANG Yun, WU Fengjiang, SUN Li, et al. Iron loss influence of induction motors on DTC performance and Its compensation method[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society,2008, 23 (9) : 51-56. |
| [14] | MUSTAFA A, OKUMUS H I. Stator resistance estimation using ANN in DTC IM drives[J]. Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences,2010, 18 (2) : 197-210. |
| [15] |
丁惜瀛, 夏强, 赵鑫, 等. 直接转矩控制磁链低频脉动分析及抑制[J].
电气技术,2008 (9) : 46-50.
DING Xiying, XIA Qing, ZHAO Xin, et al. Analysis and restrain of low frequency ripple for direct torque control of flux linkage[J]. Electrical Engineering,2008 (9) : 46-50. |
| [16] | ZIDANI F, DIALLO D, BENBOUZID M E H, et al. Direct torque control of induction motor with fuzzy stator resistance adaptation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion,2006, 21 (2) : 619-621. DOI: 10.1109/TEC.2006.874251 |
 2016, Vol. 48
2016, Vol. 48


